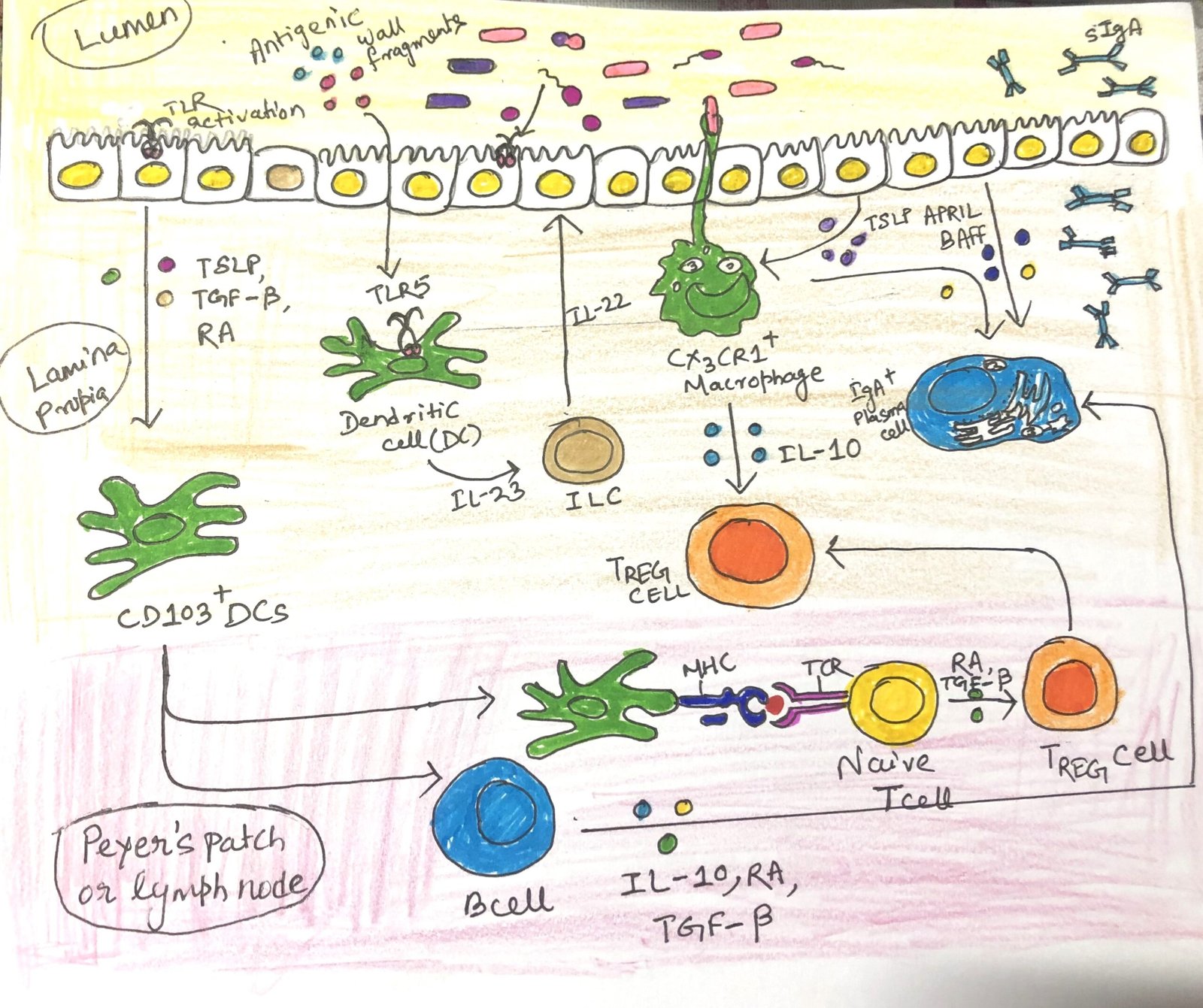
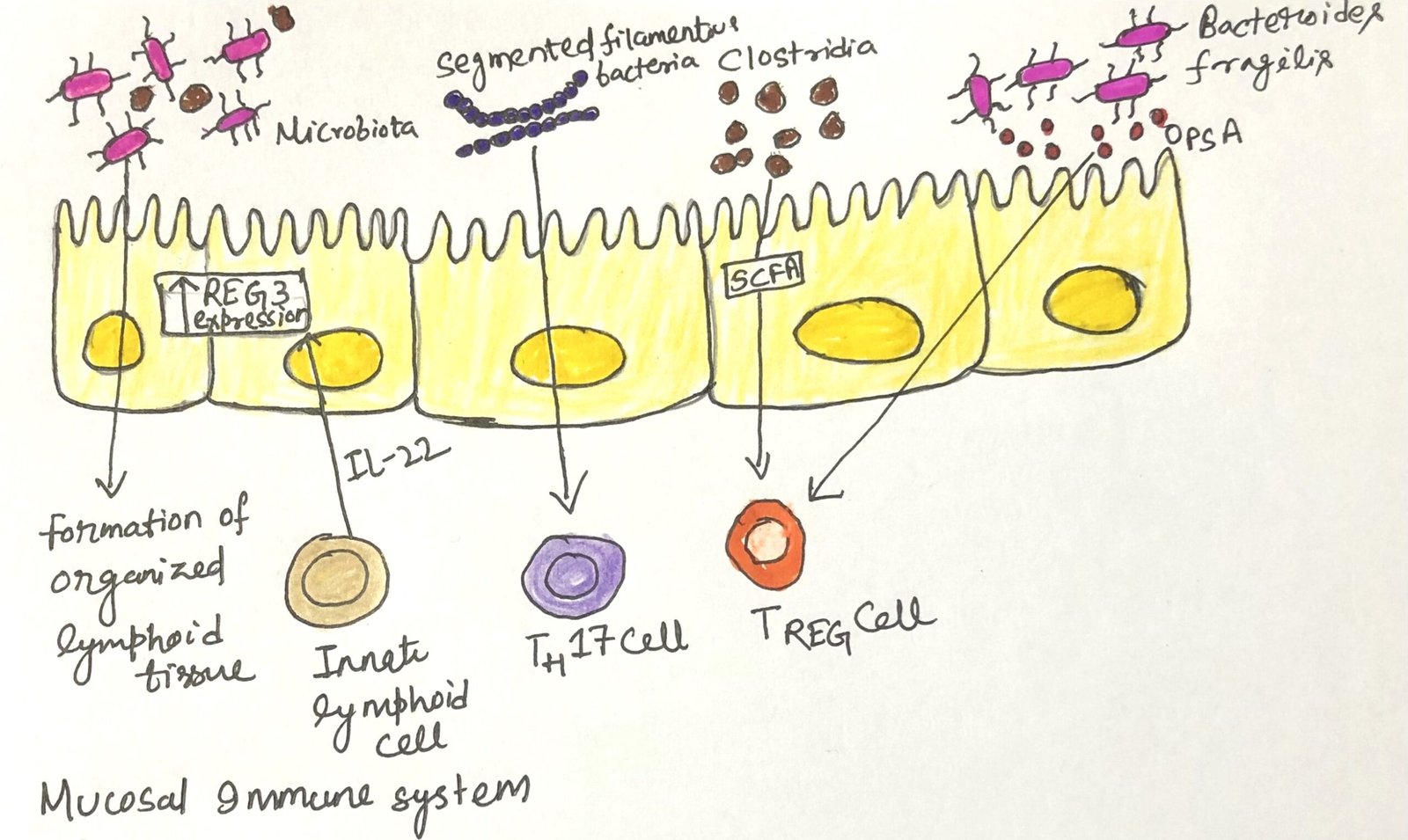
The Skin Immune System
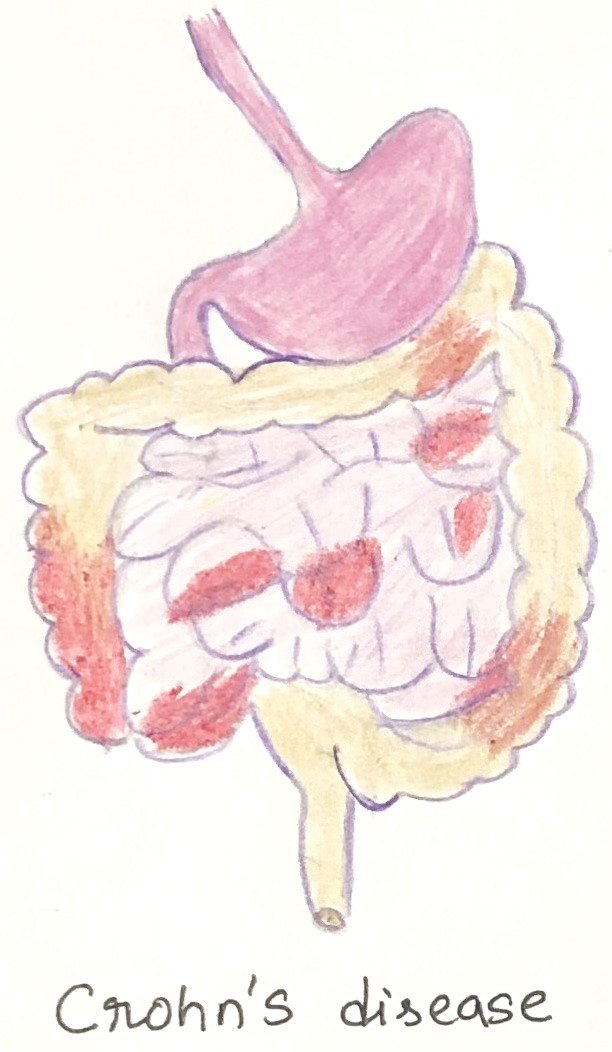
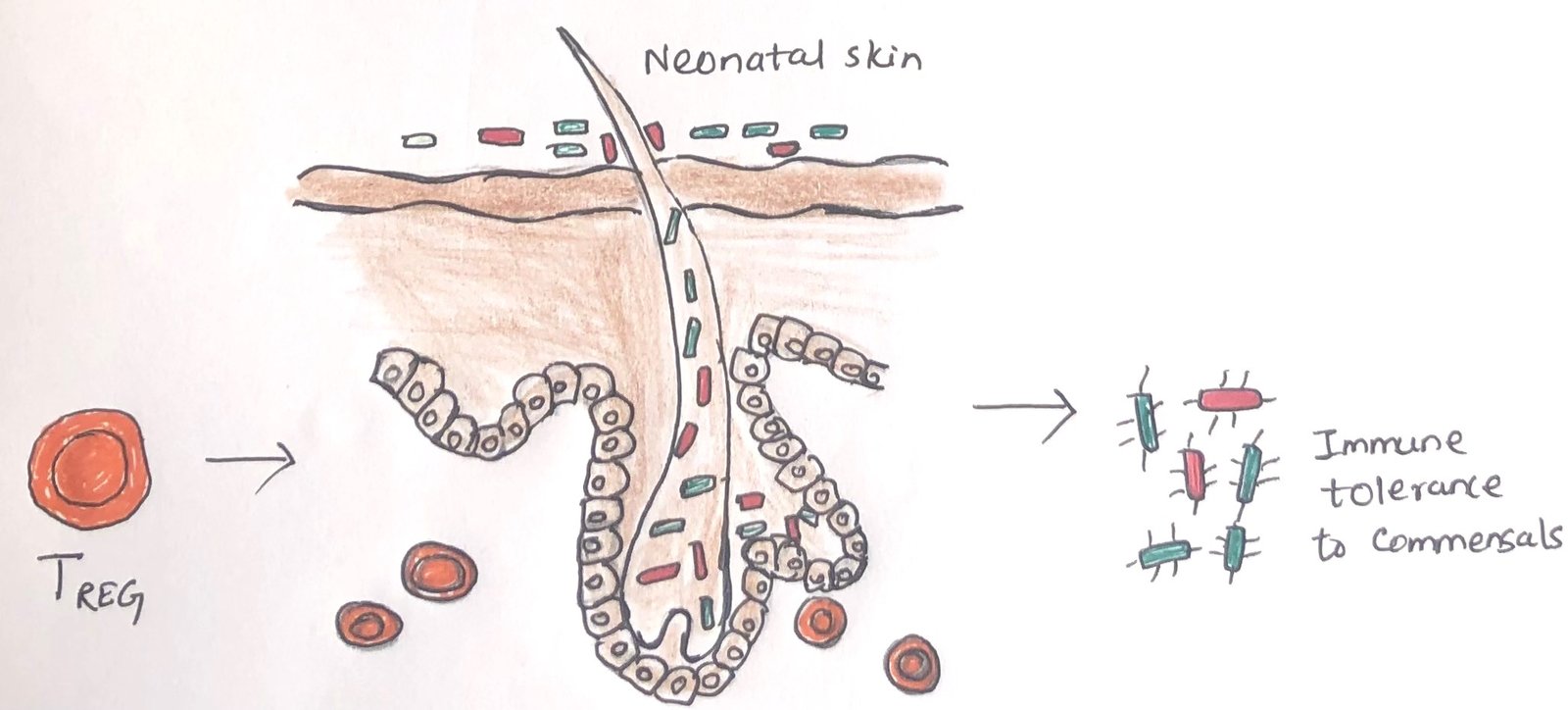
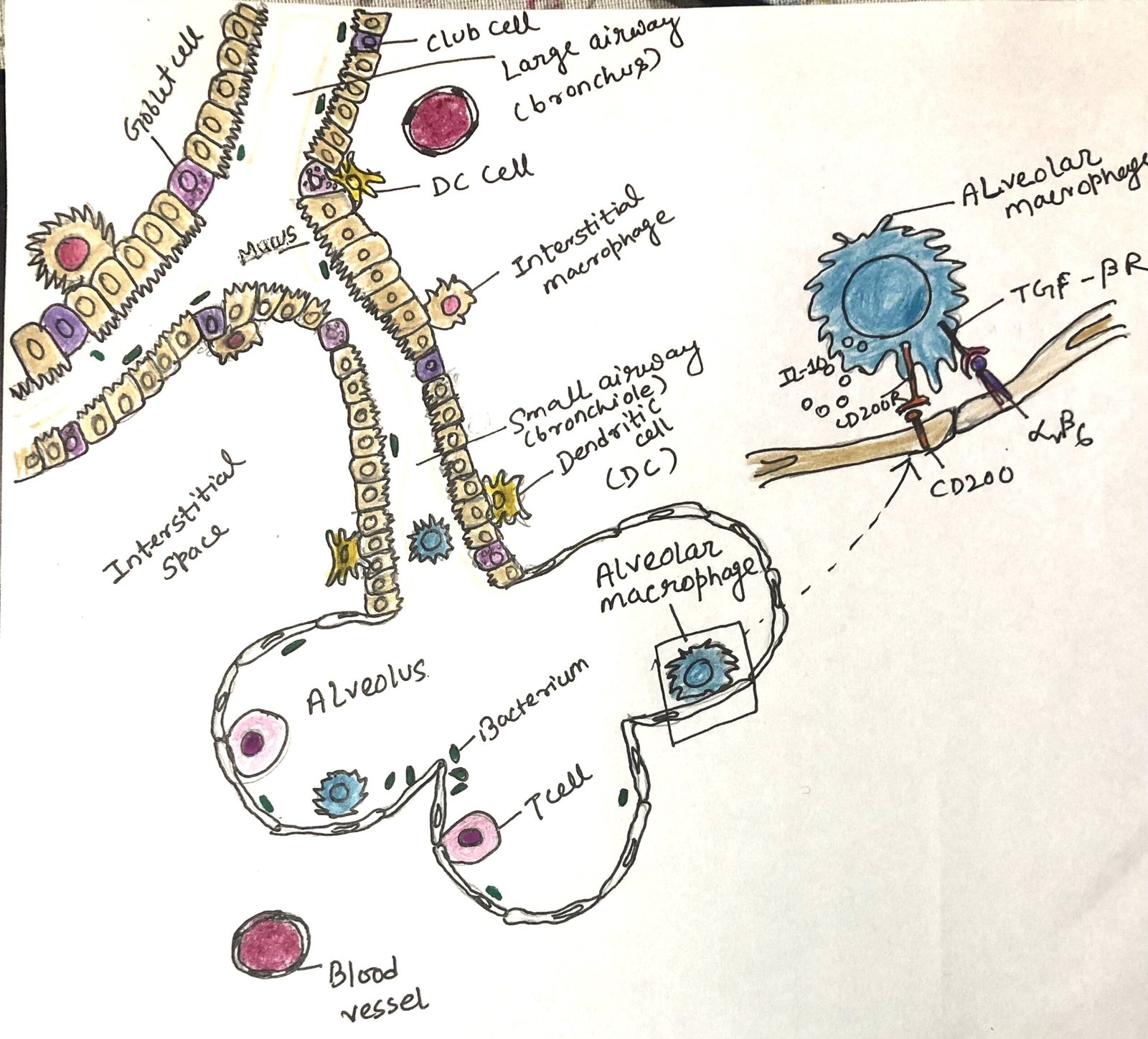
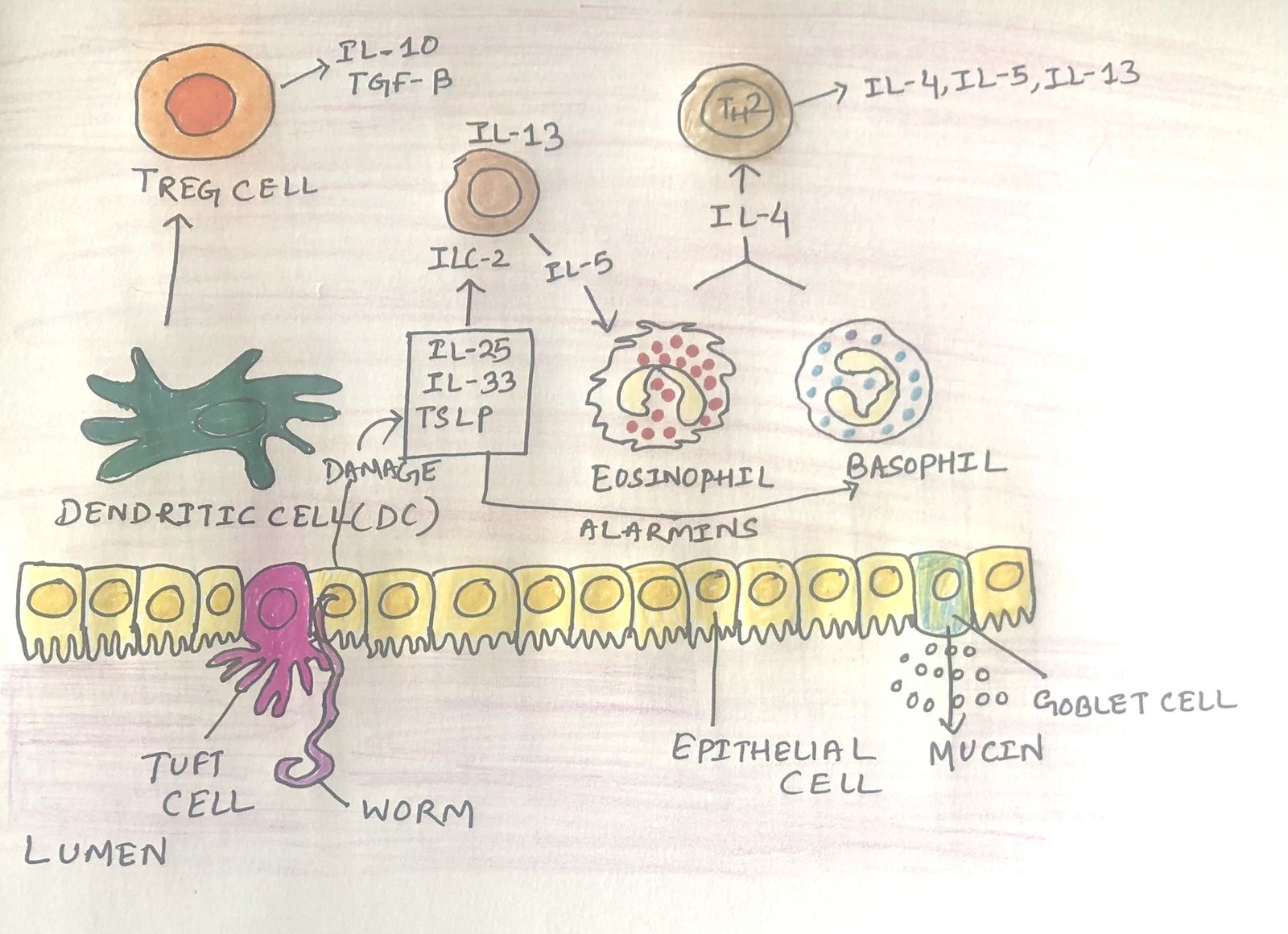
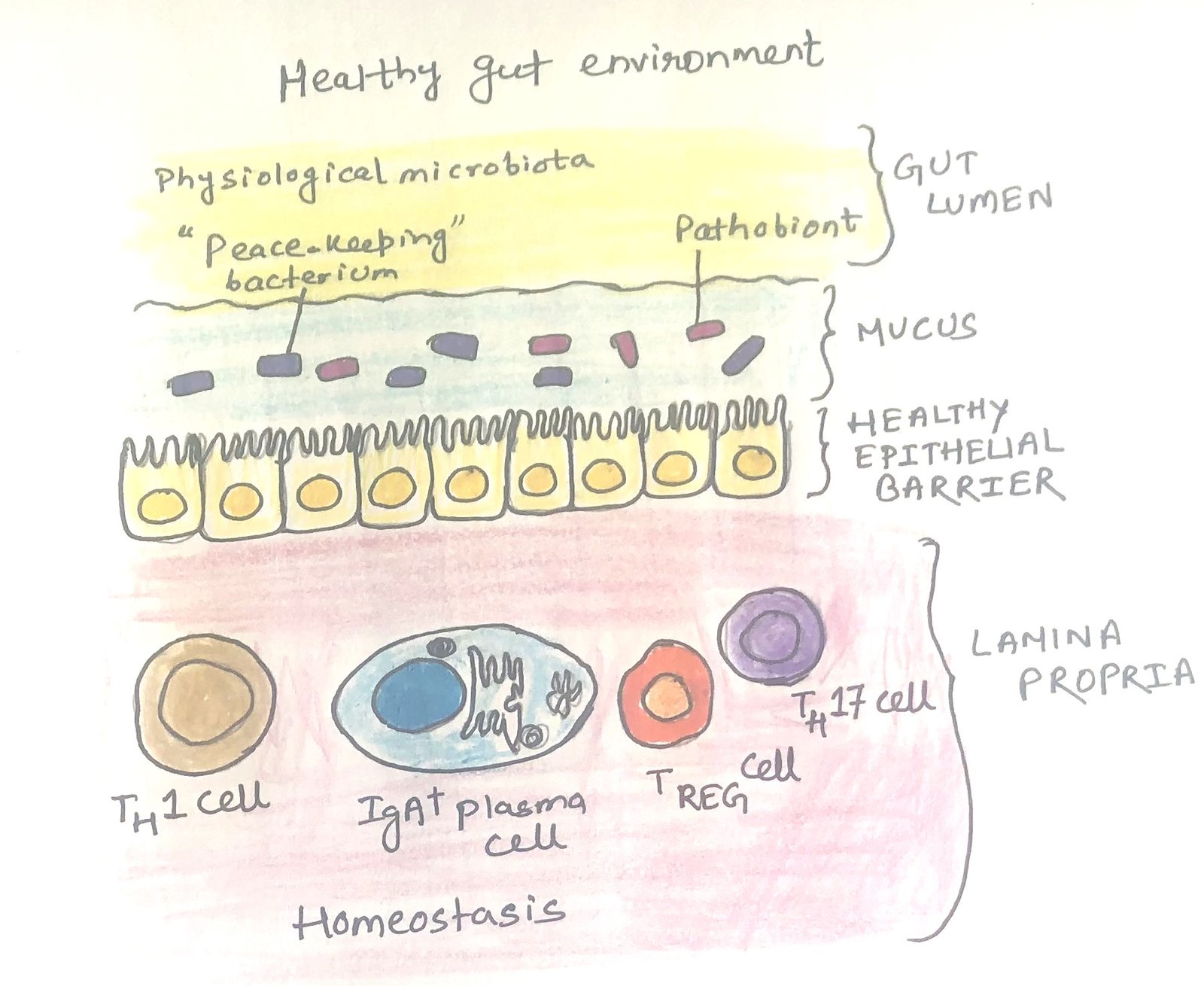
In this article, I briefly describe the skin immune system and its similarities and dissimilarities with the respiratory and intestinal immune systems. Skin The bodies of vertebrate animals are covered with a soft, flexible outer tissue layer called skin. It serves three primary roles: protection, regulation, and sensation. The skin interacts directly with the environment, … Read more >>