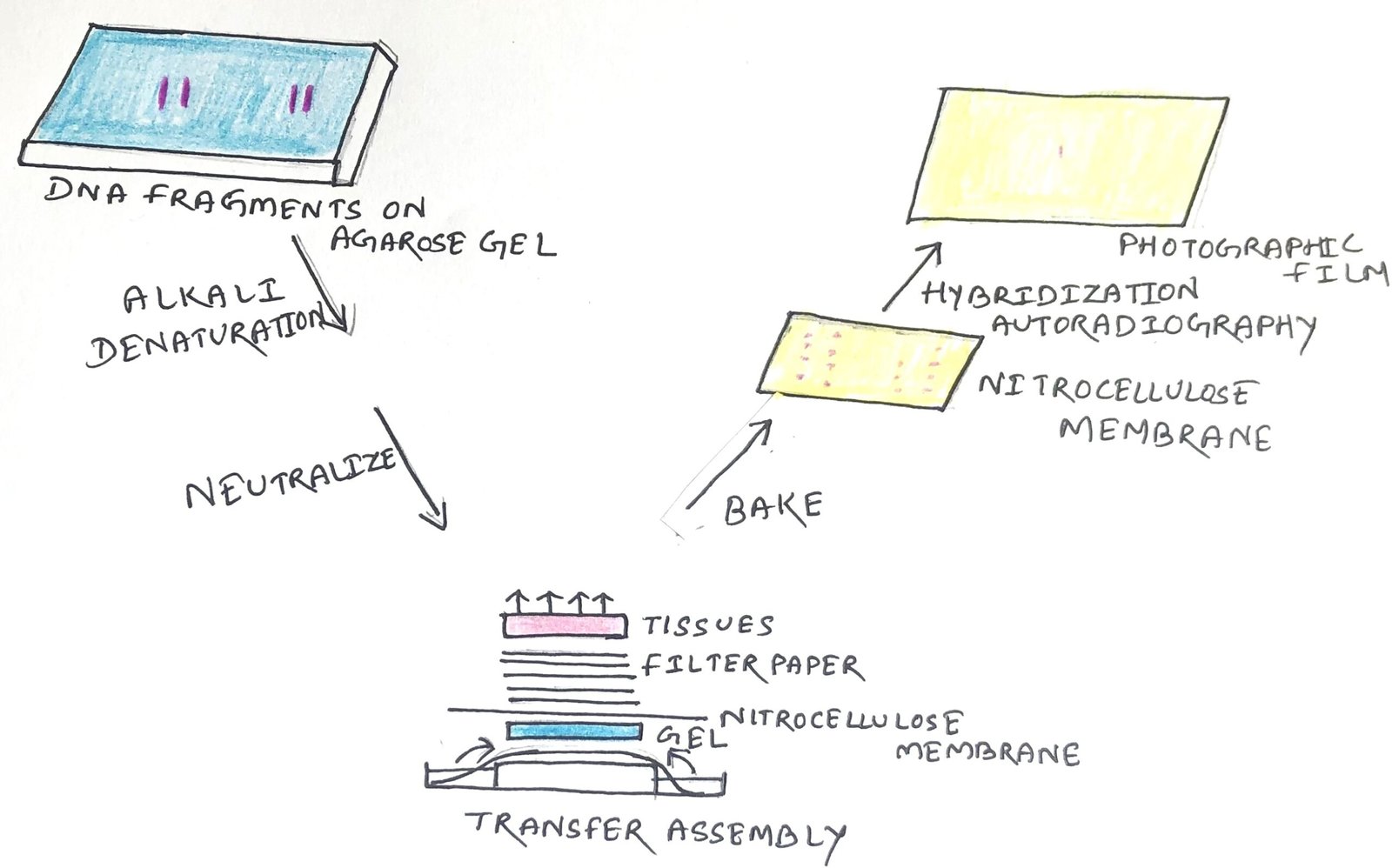
Northern blotting: Detection of RNA
In this article, I briefly describe Northern blotting and its applications. Northern blotting It is a laboratory technique, which studies gene expression by detecting a specific RNA sequence in a blood or tissue sample. Northern blotting was first developed in 1977 by James Alwine, David Kemp, and George Stark at Stanford University. The name was … Read more >>