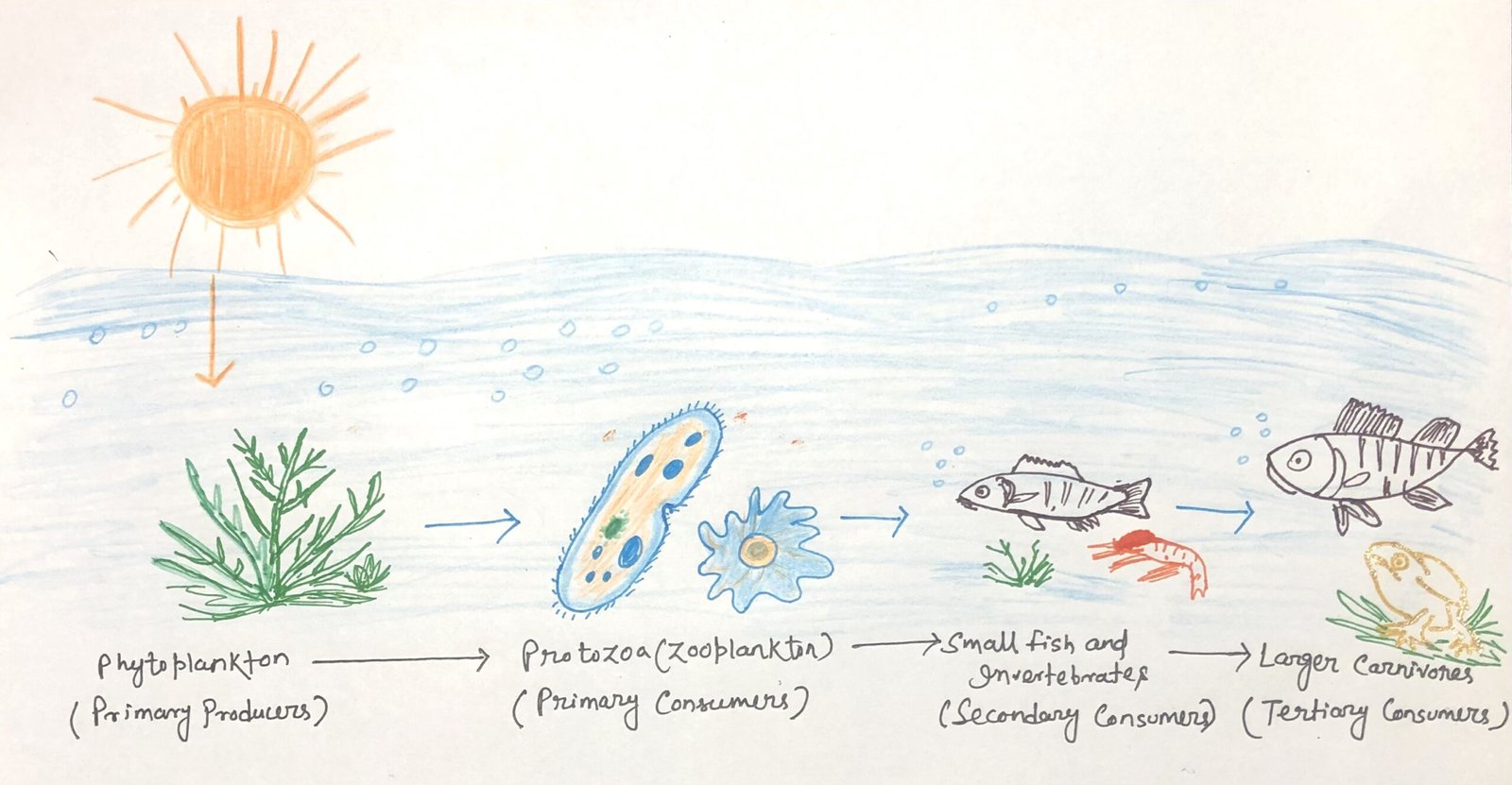
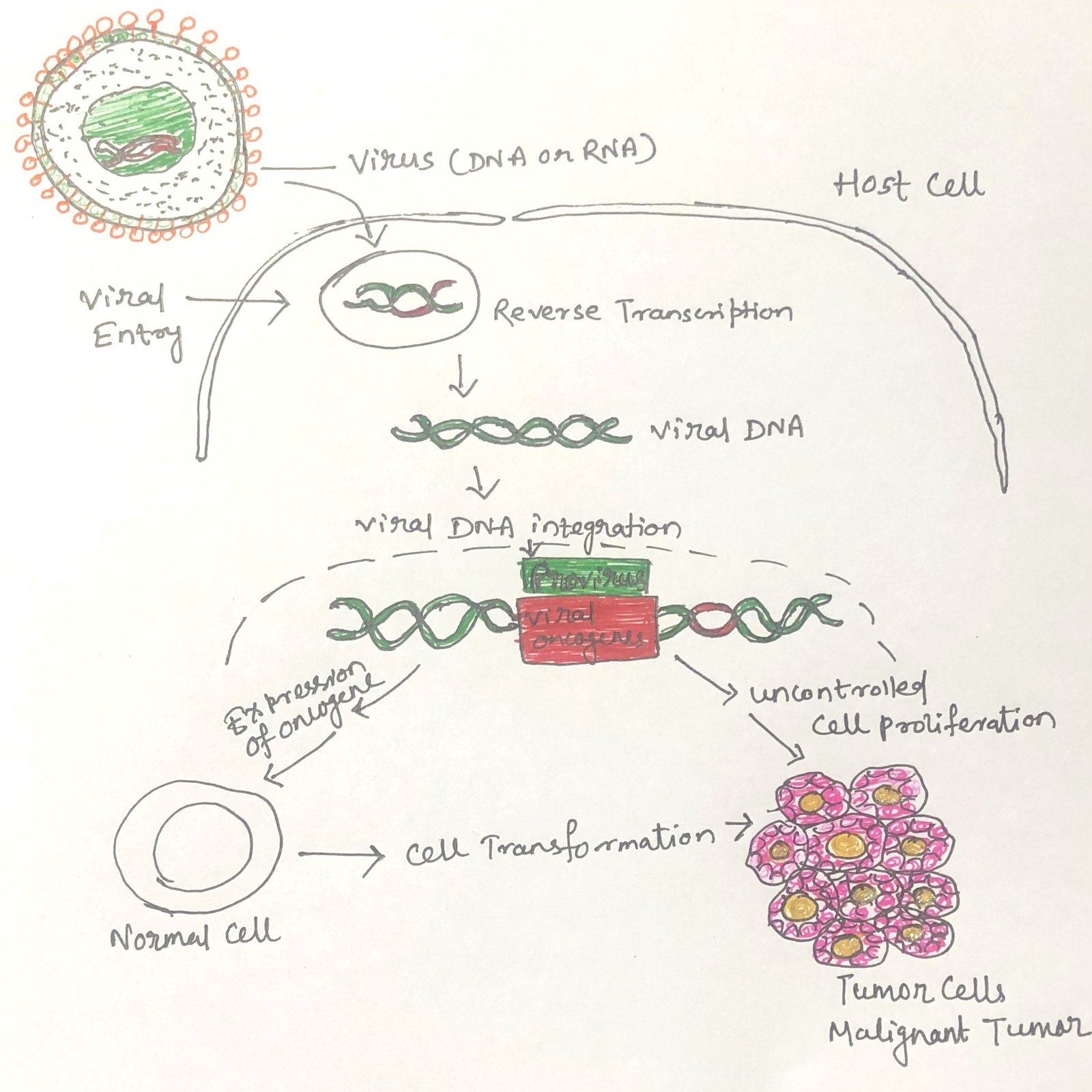
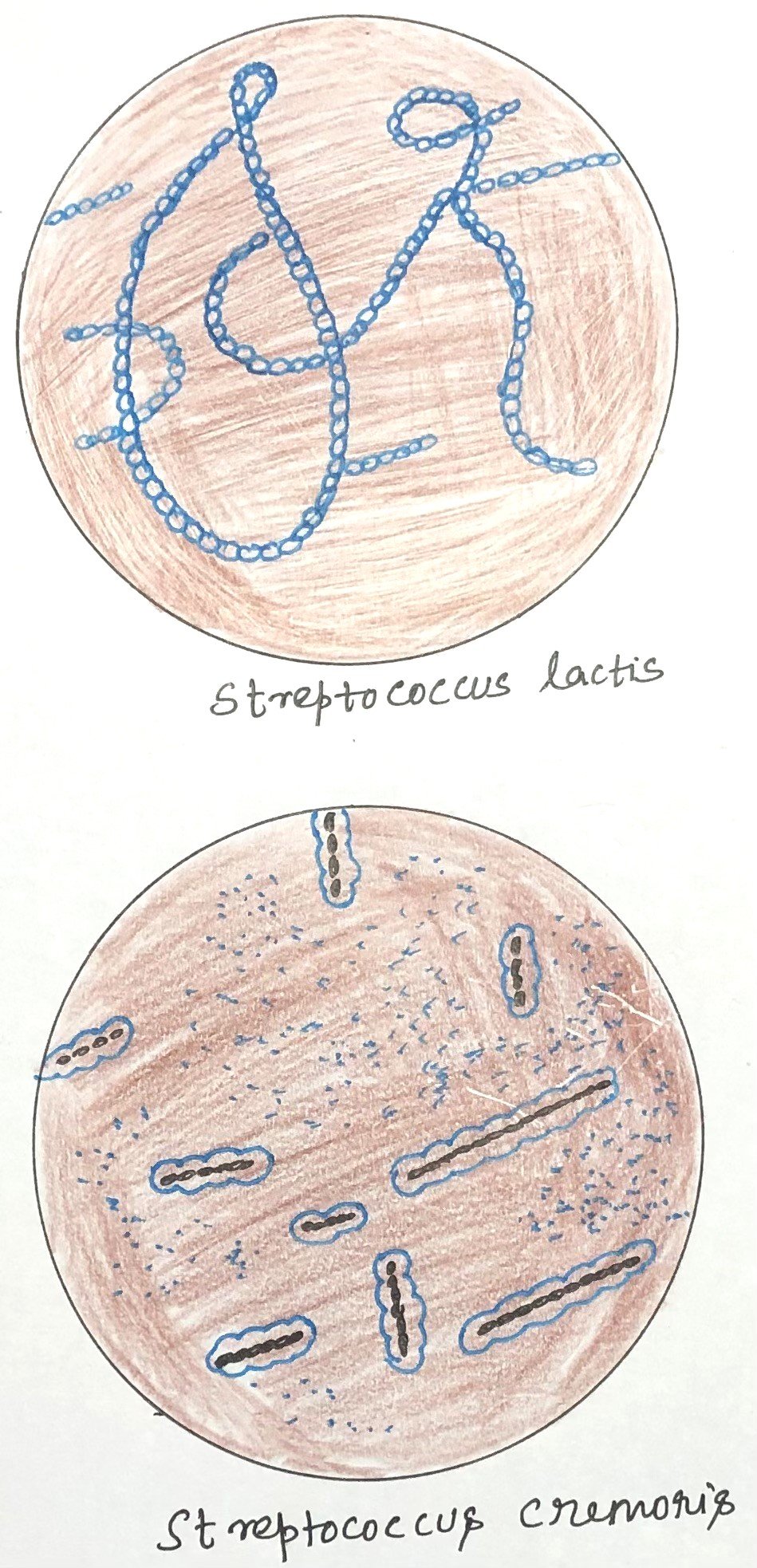
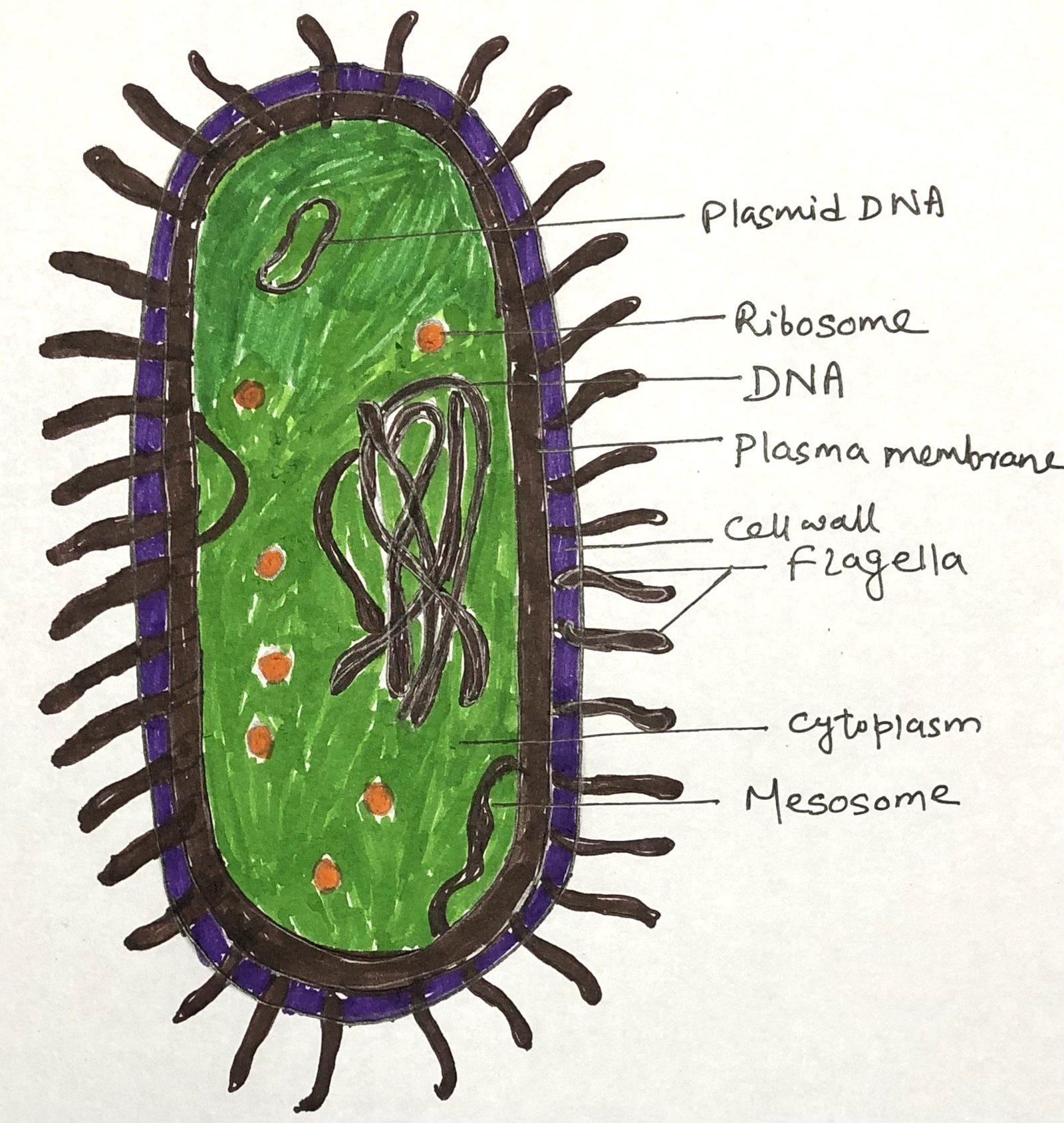
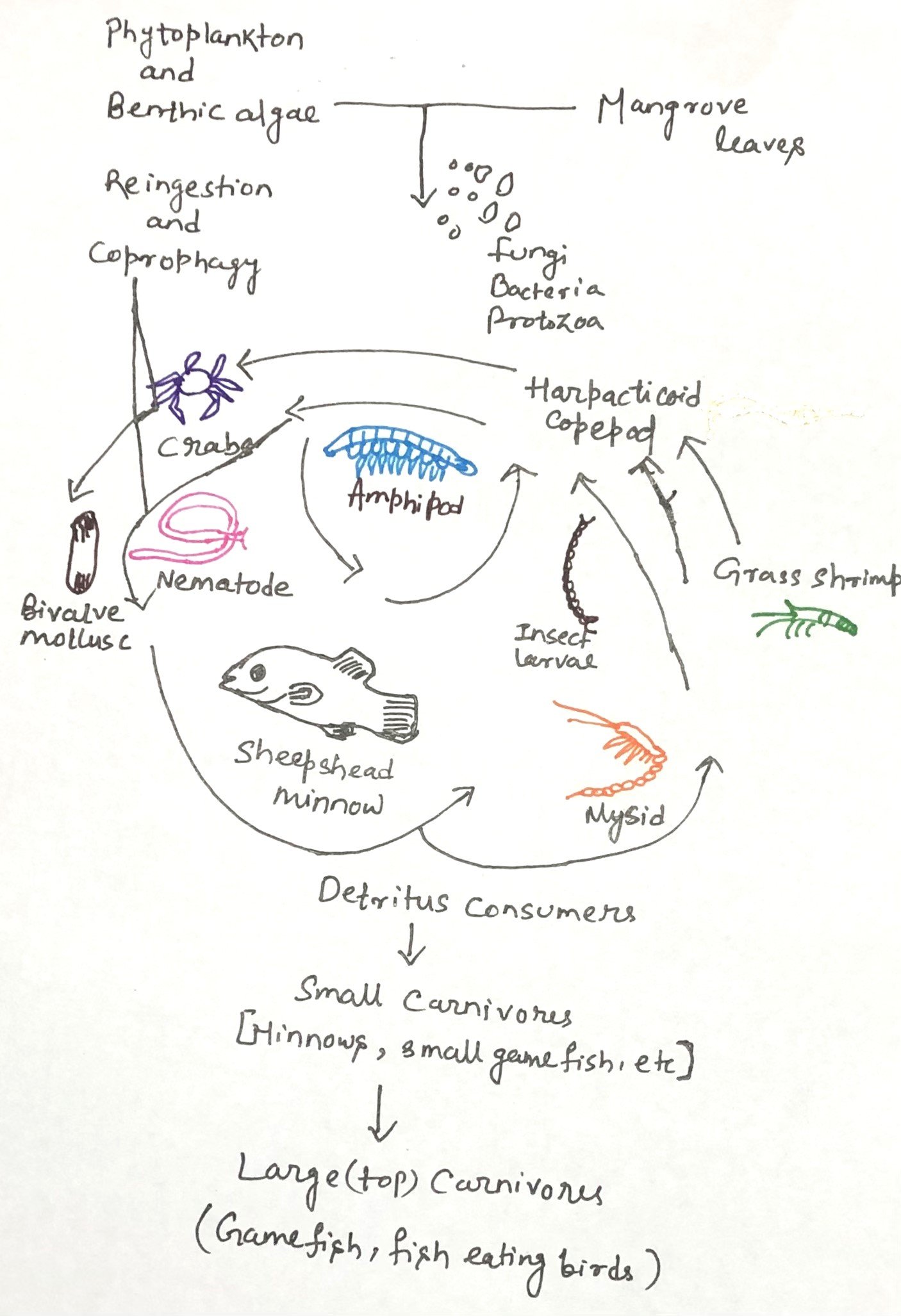
Protozoa in Nature and Their Ecological Significance
In this article, I briefly describe protozoa and their ecological significance. Protozoa are microscopic yet remarkably diverse organisms that occupy nearly every habitat on Earth. Despite their small size, they play a profound role in maintaining ecological balance and influencing both environmental processes and human health. The Widespread World of Protozoa Protozoa inhabit nearly all … Read more >>