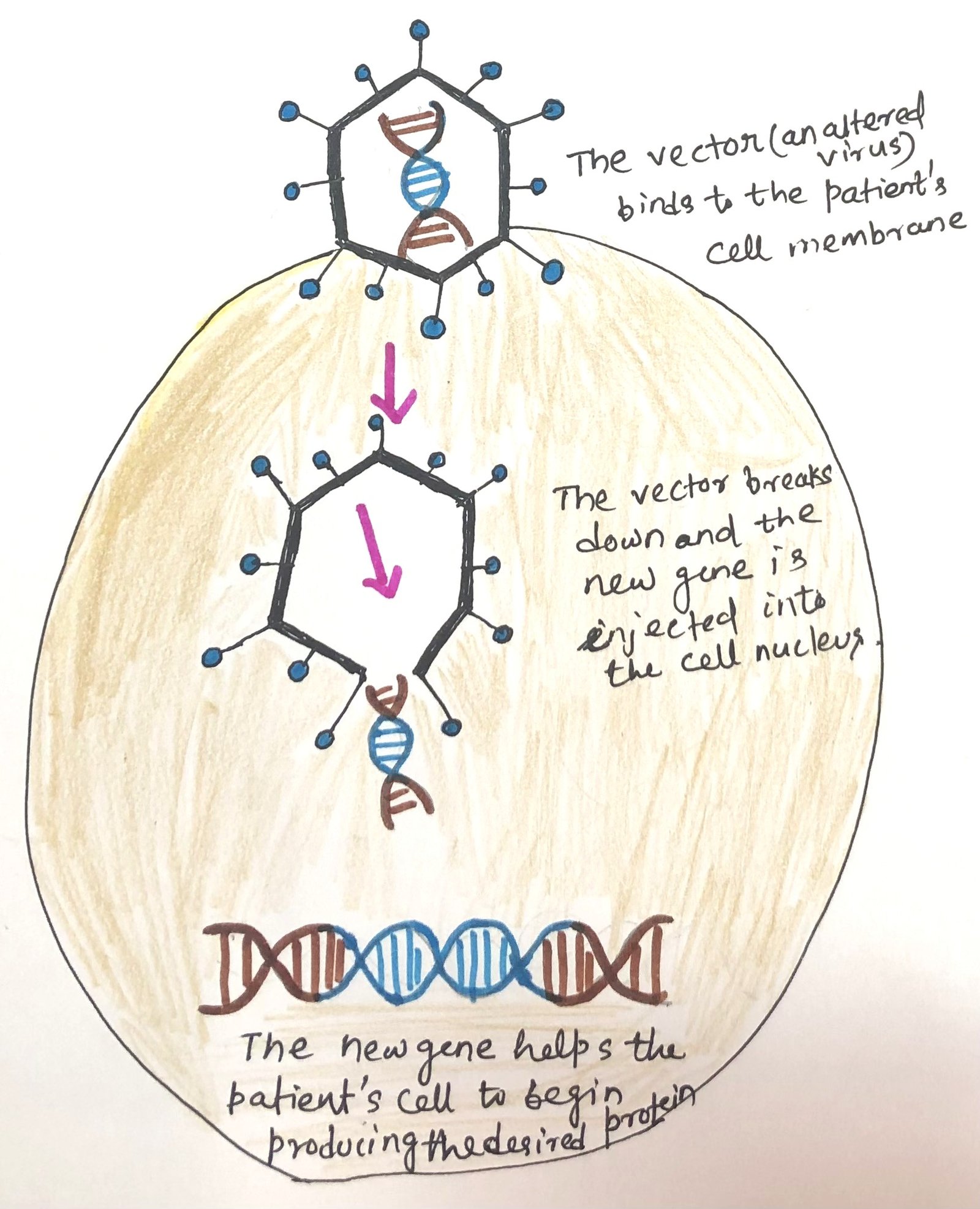
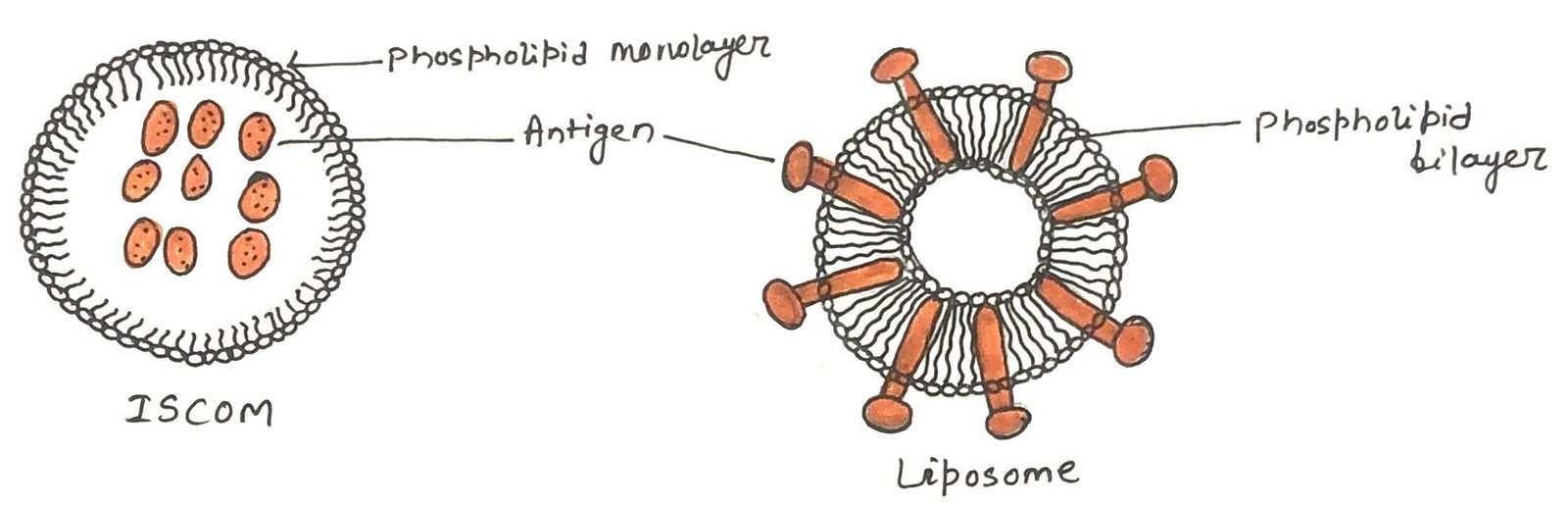
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infects Its Host by Using Co-receptors
In this article, I briefly describe how HIV infects its host by using its coreceptors. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a severe immunodeficiency caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This syndrome was first recognized because of opportunistic infections in a cluster of individuals in the USA in 1981. This group … Read more >>