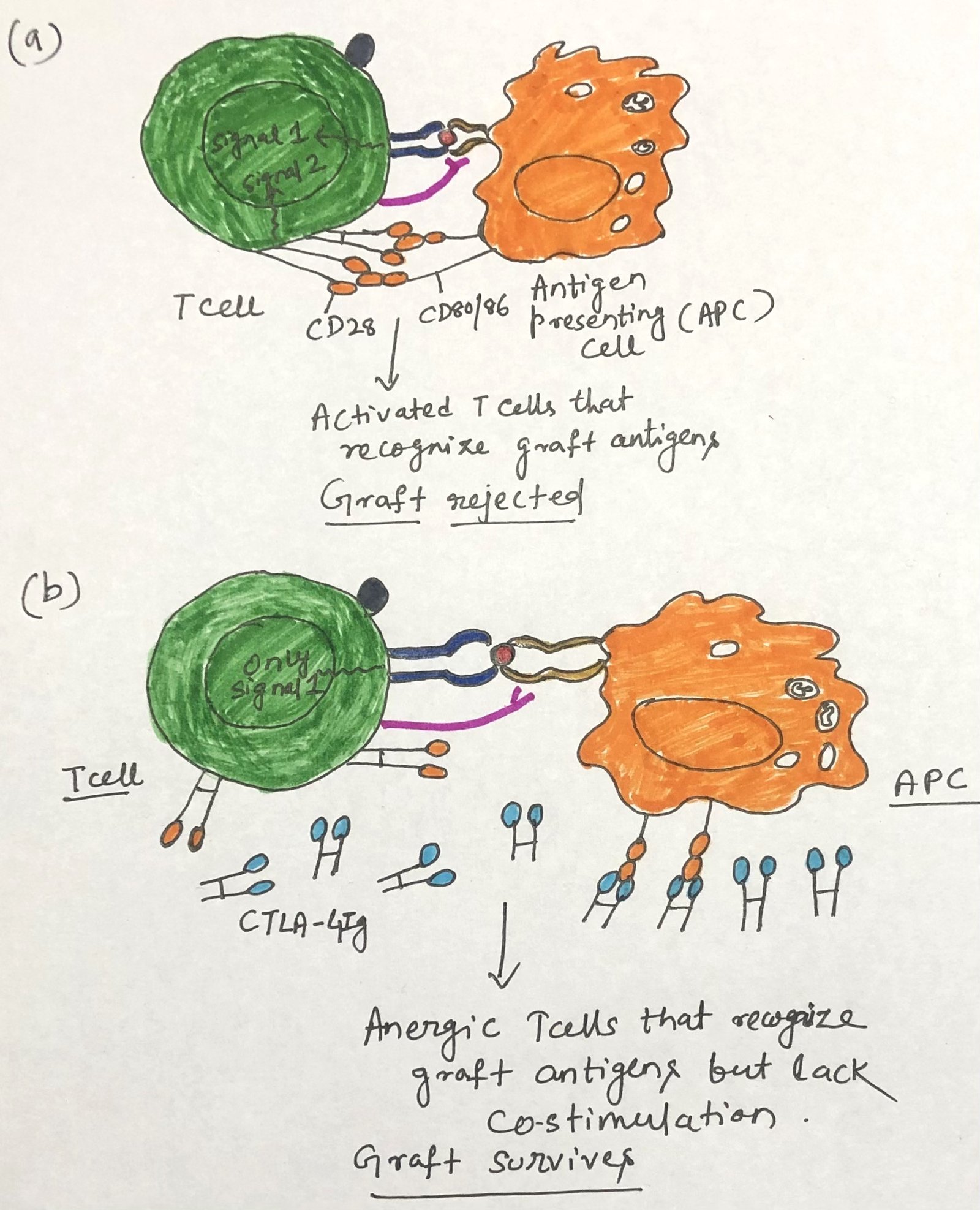
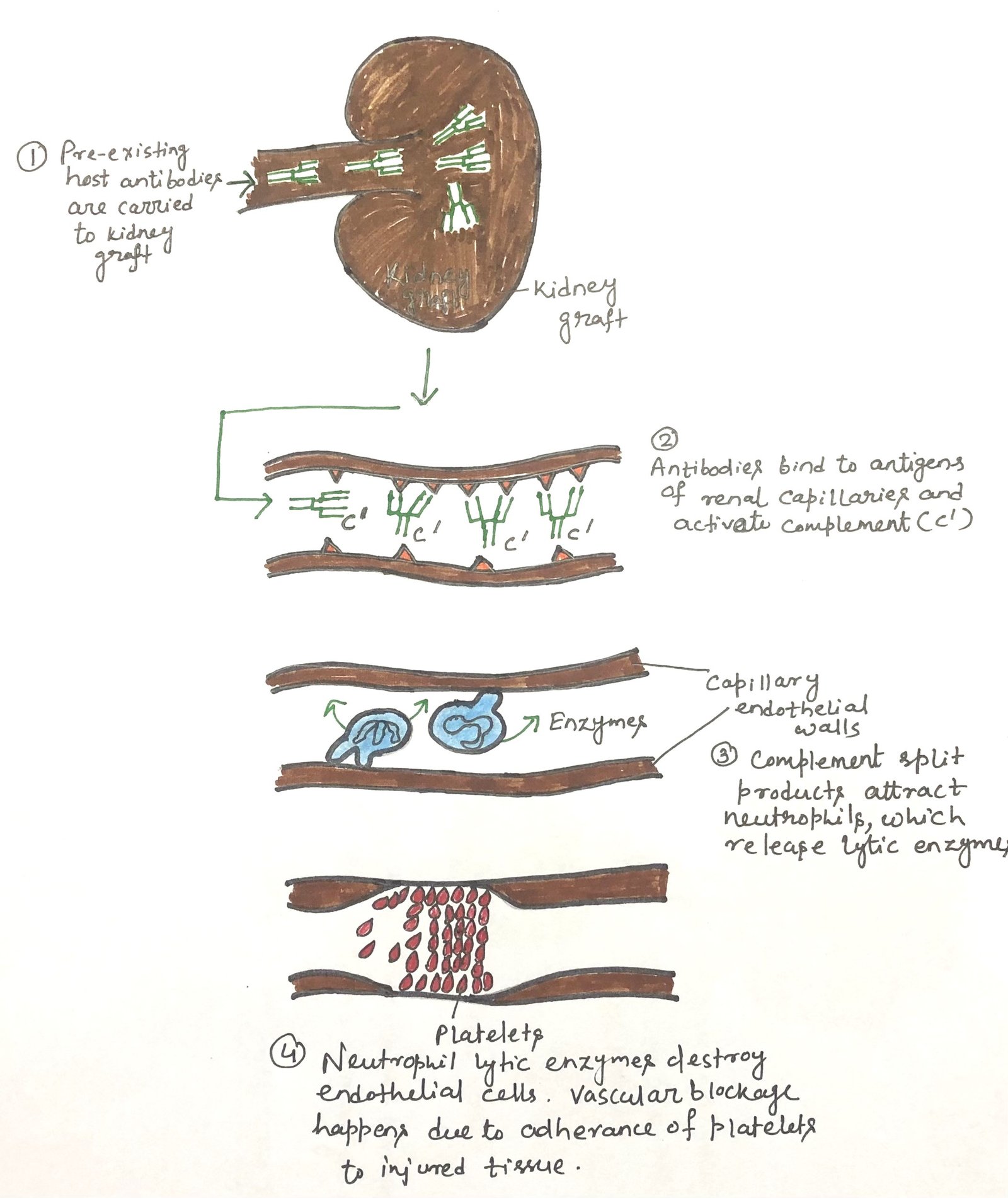
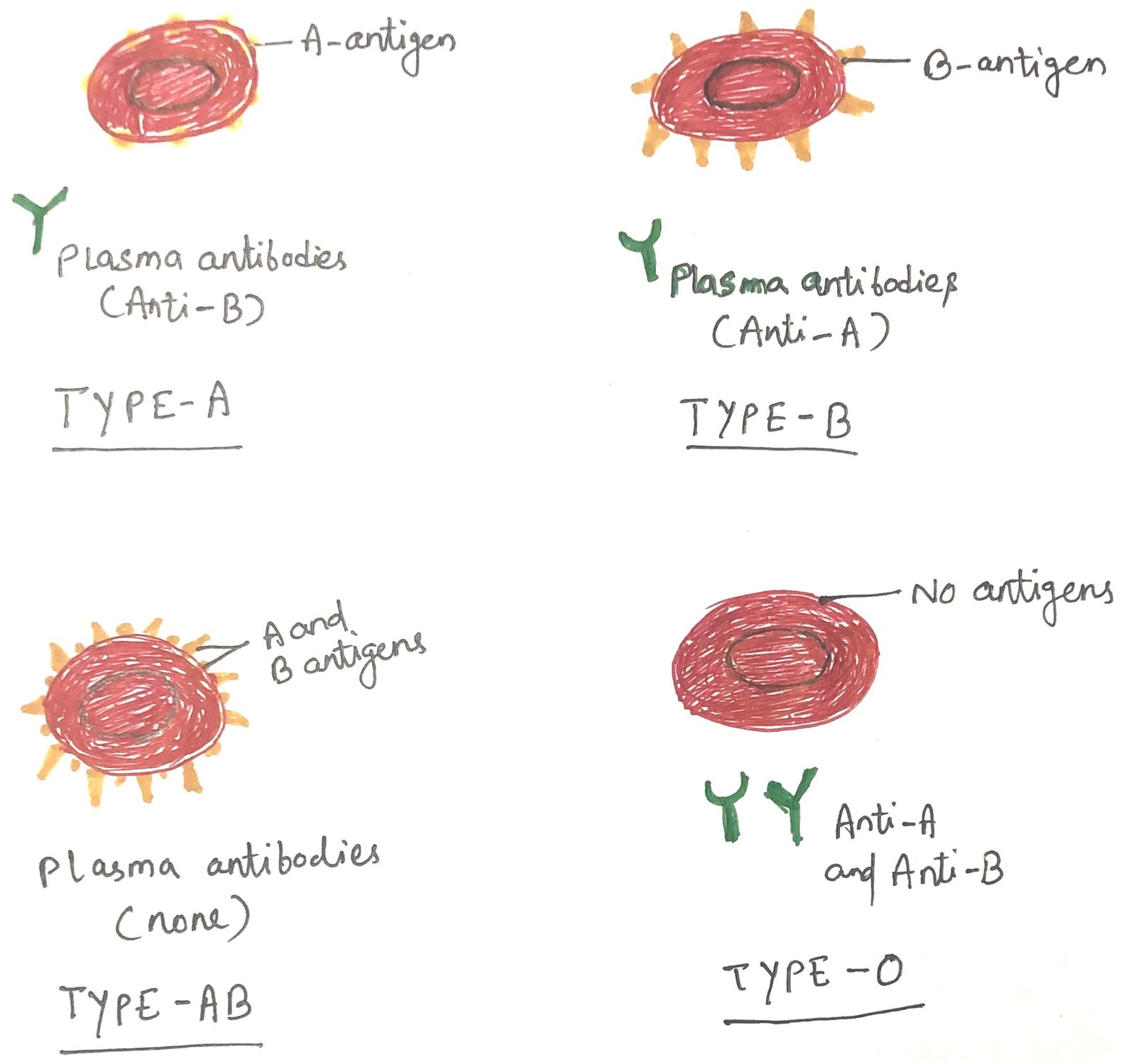
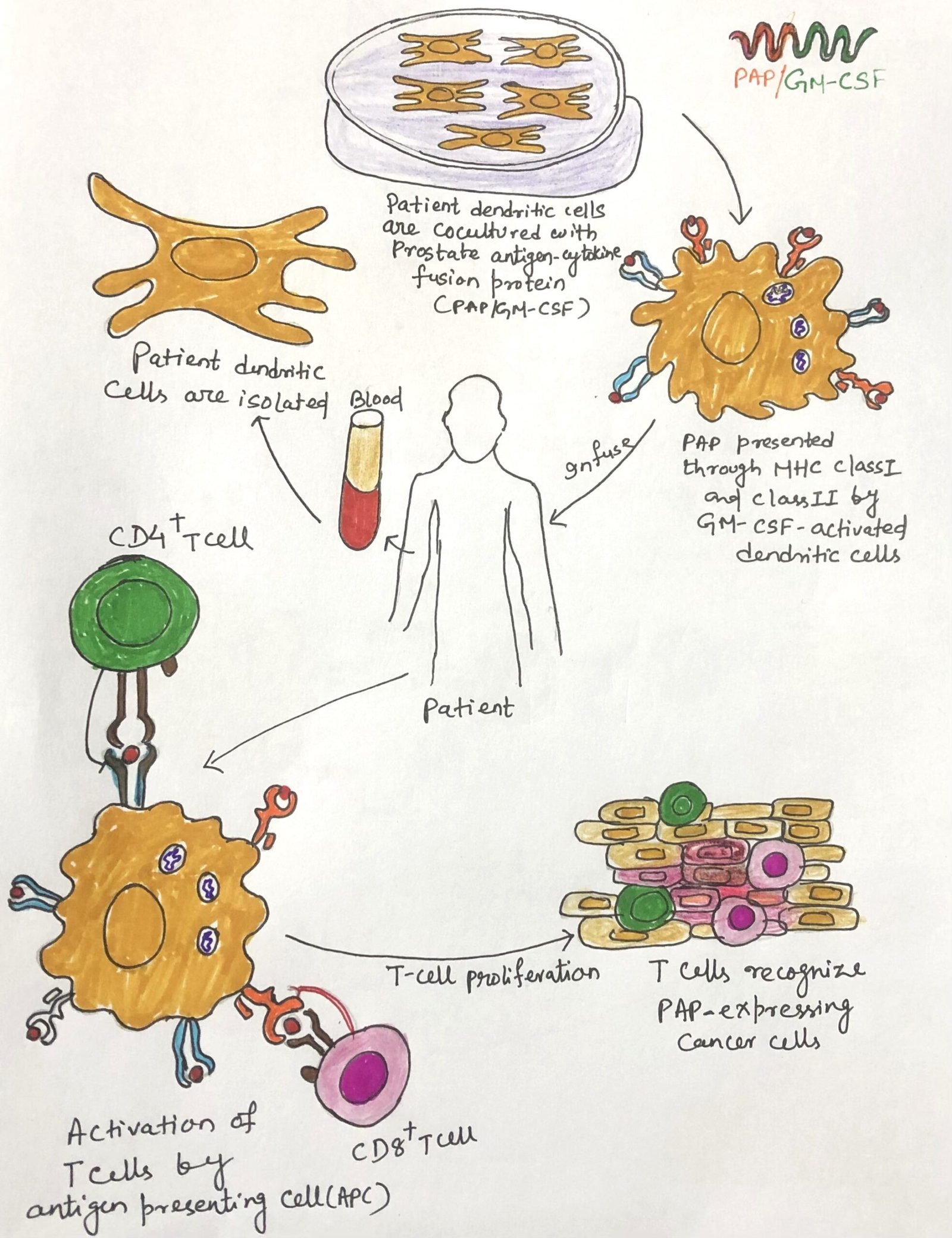
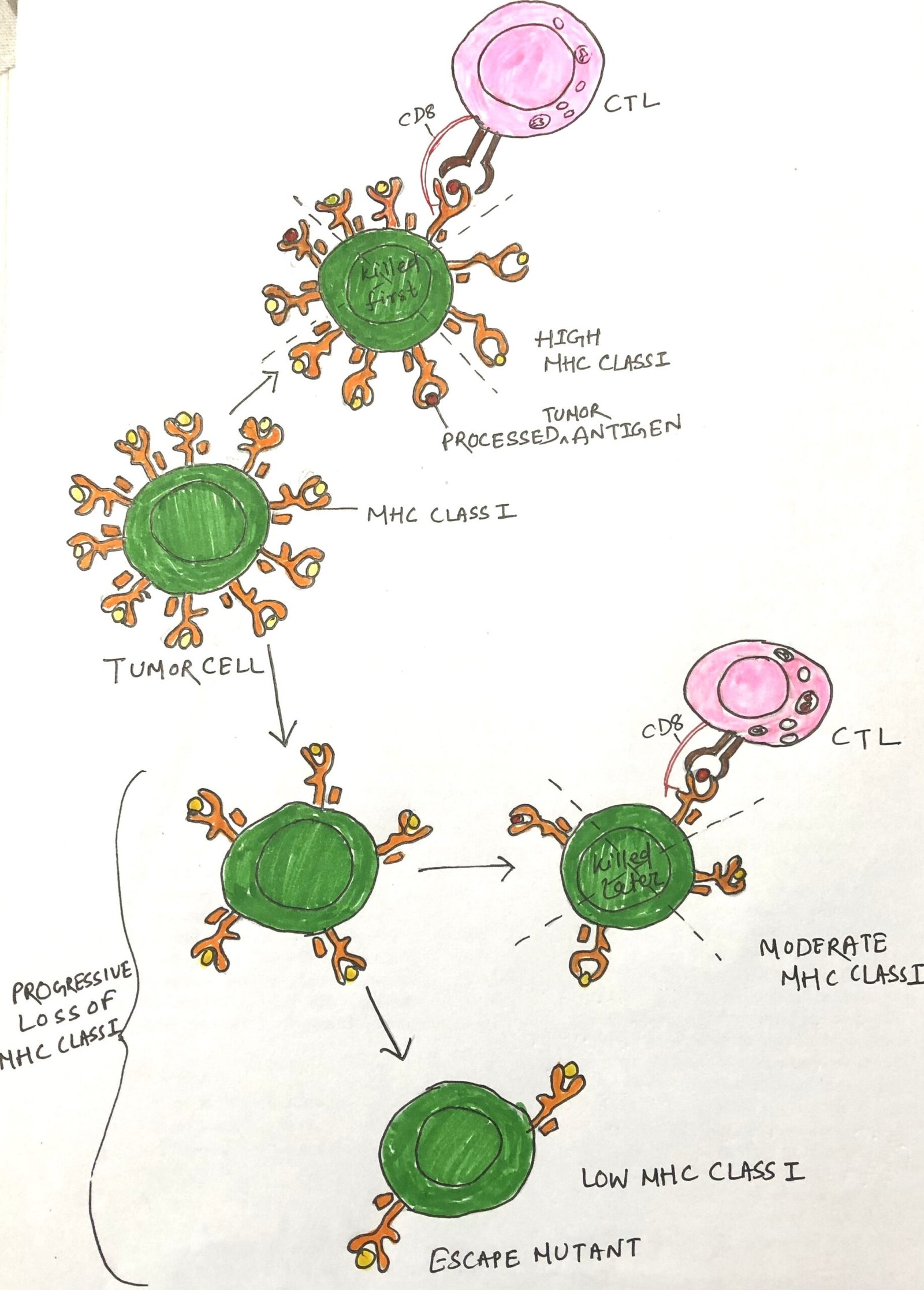
Generation of Peripheral Tolerance
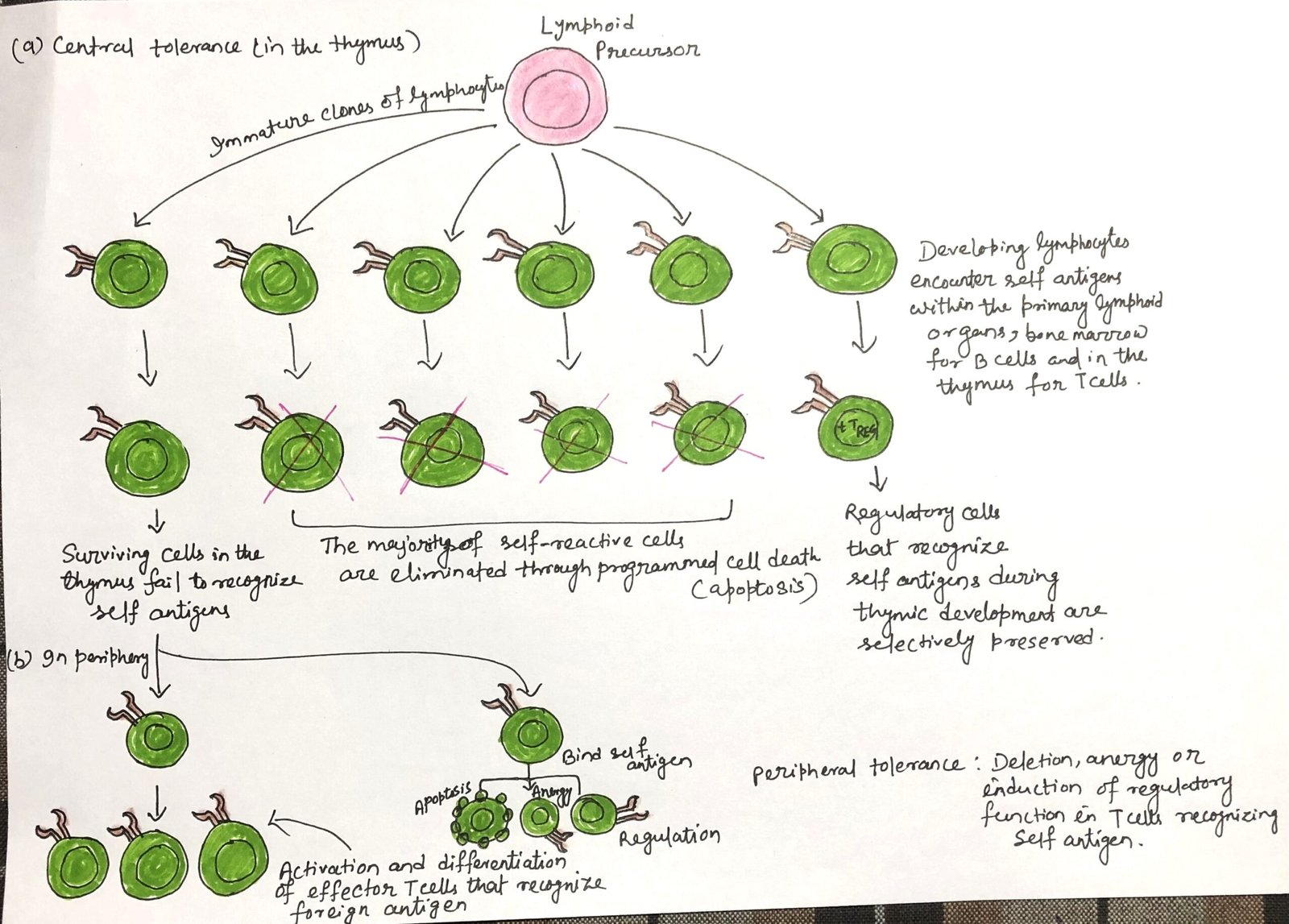
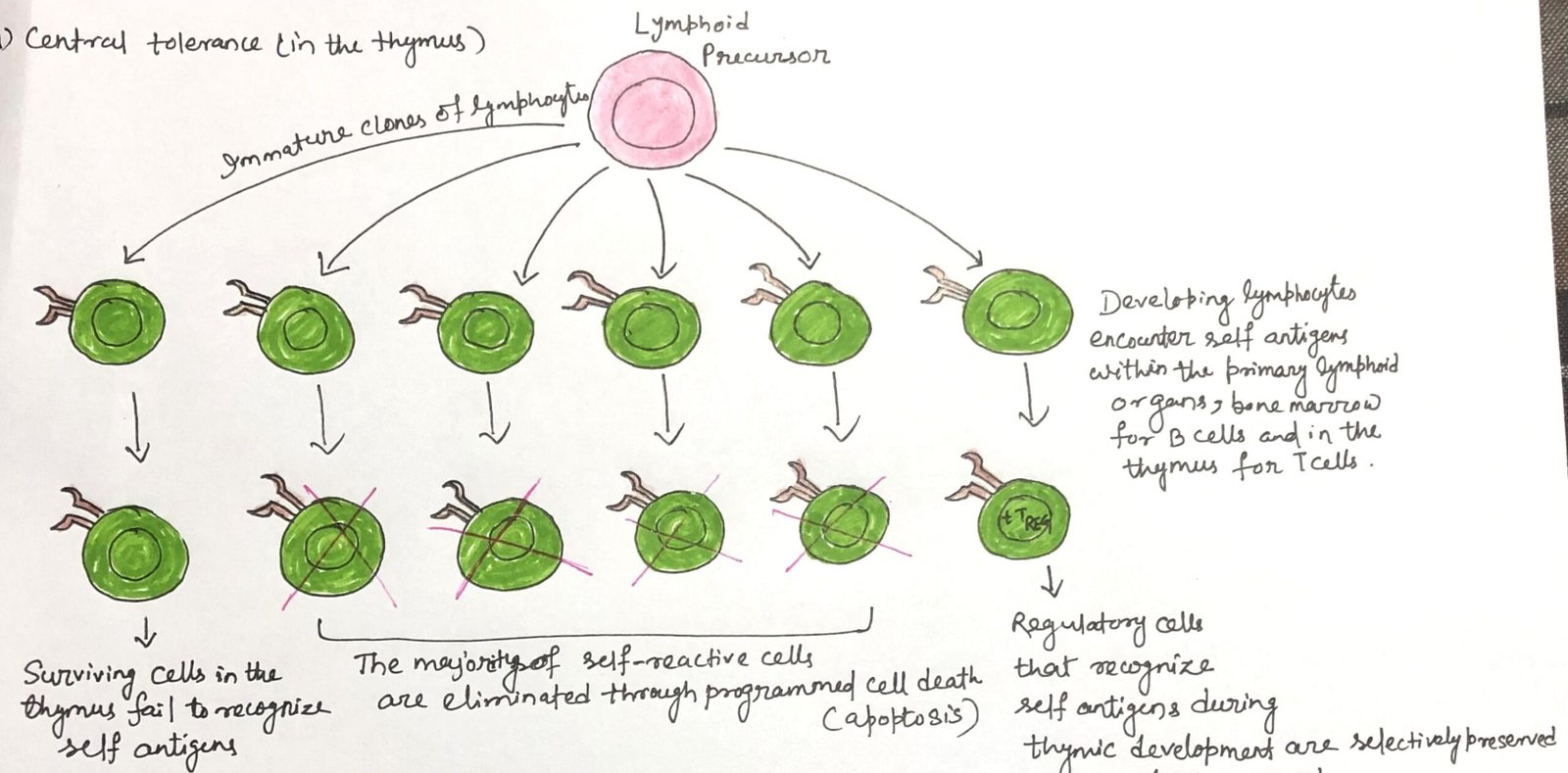
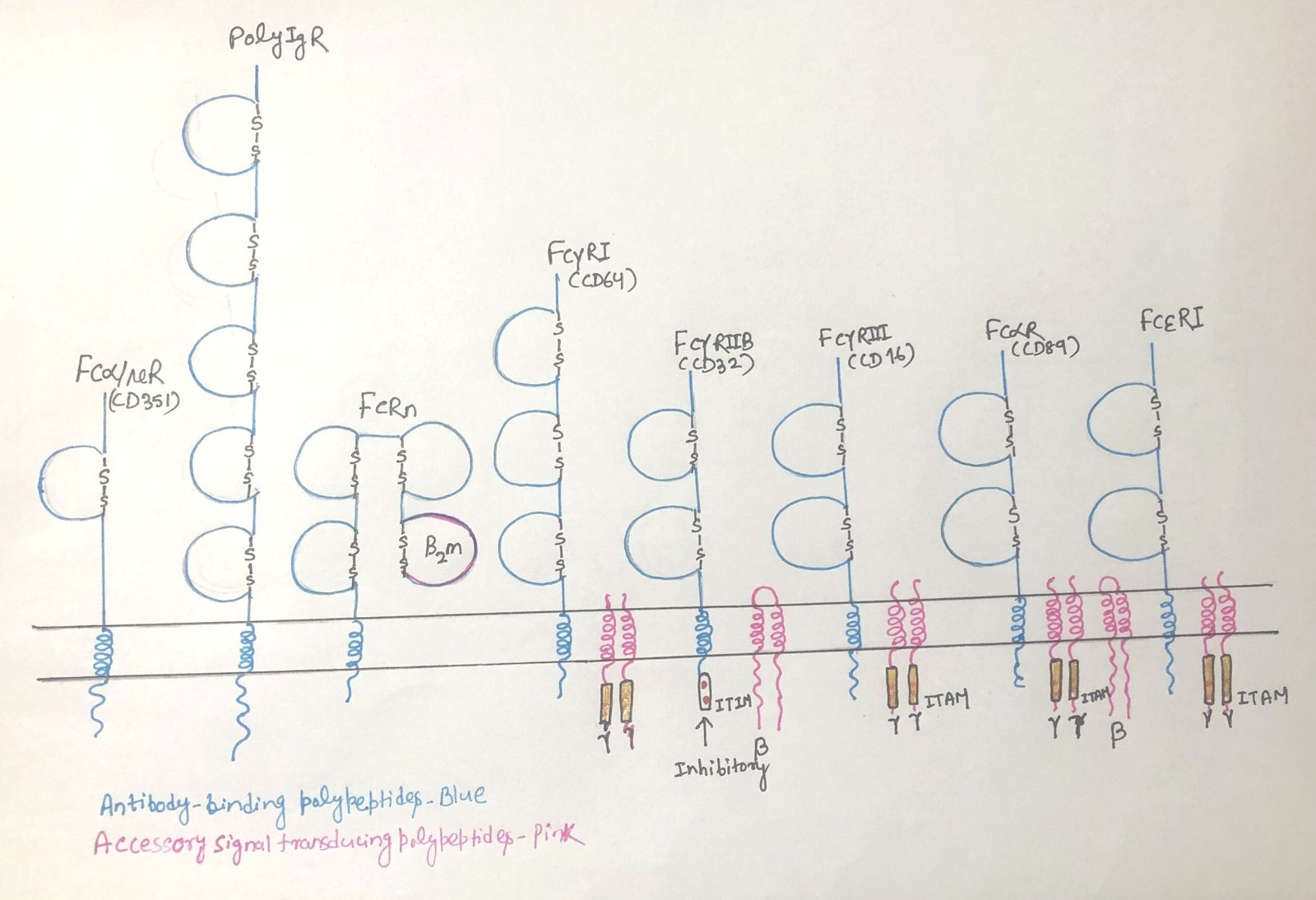
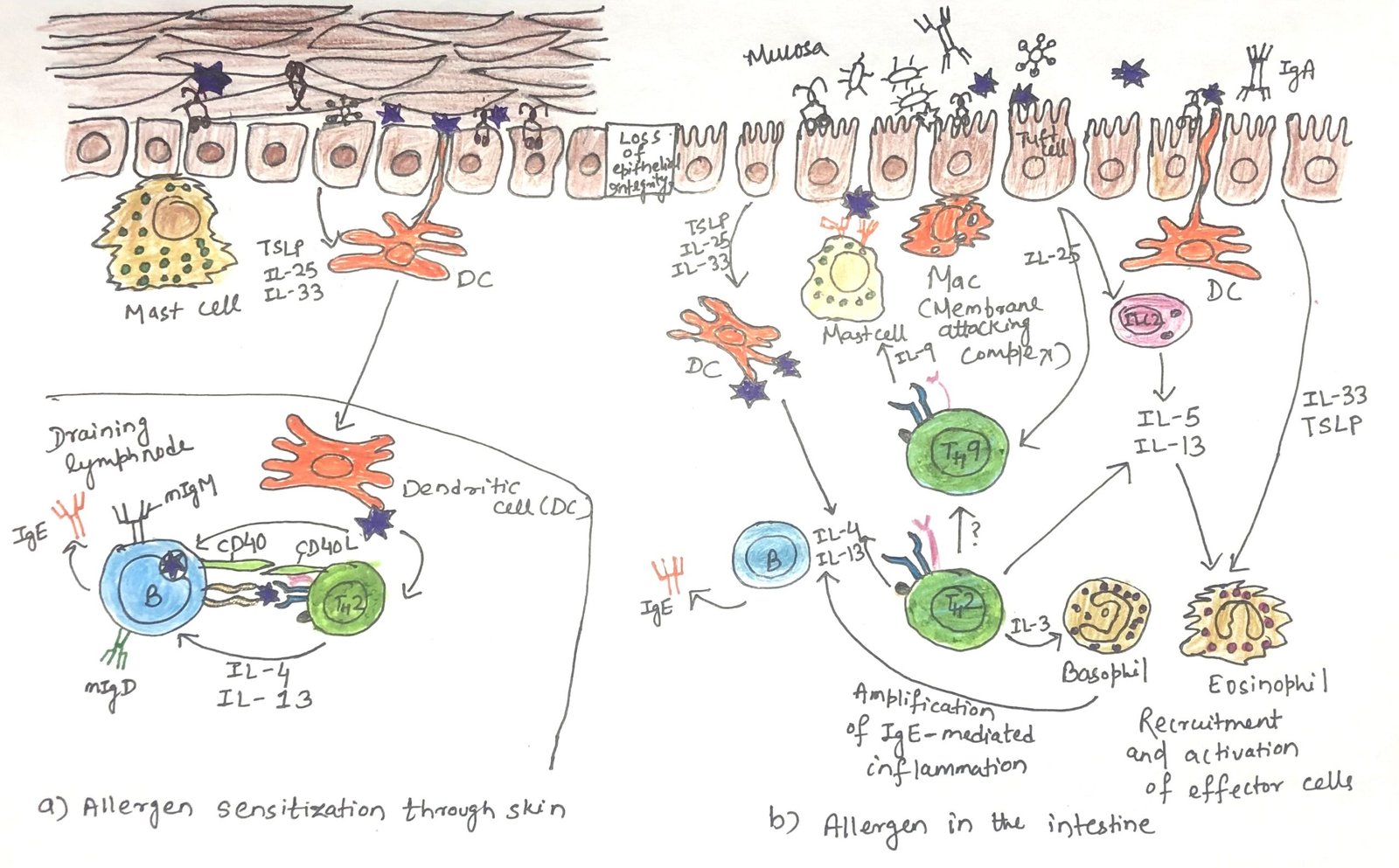
In this article, I briefly describe the generation of peripheral tolerance. It refers to the mechanisms that regulate self-reactive lymphocytes after they leave the primary lymphoid organs. It ensures that immune responses against the body’s own tissues are prevented through processes such as anergy, suppression by regulatory cells, and controlled antigen presentation. These mechanisms help … Read more >>