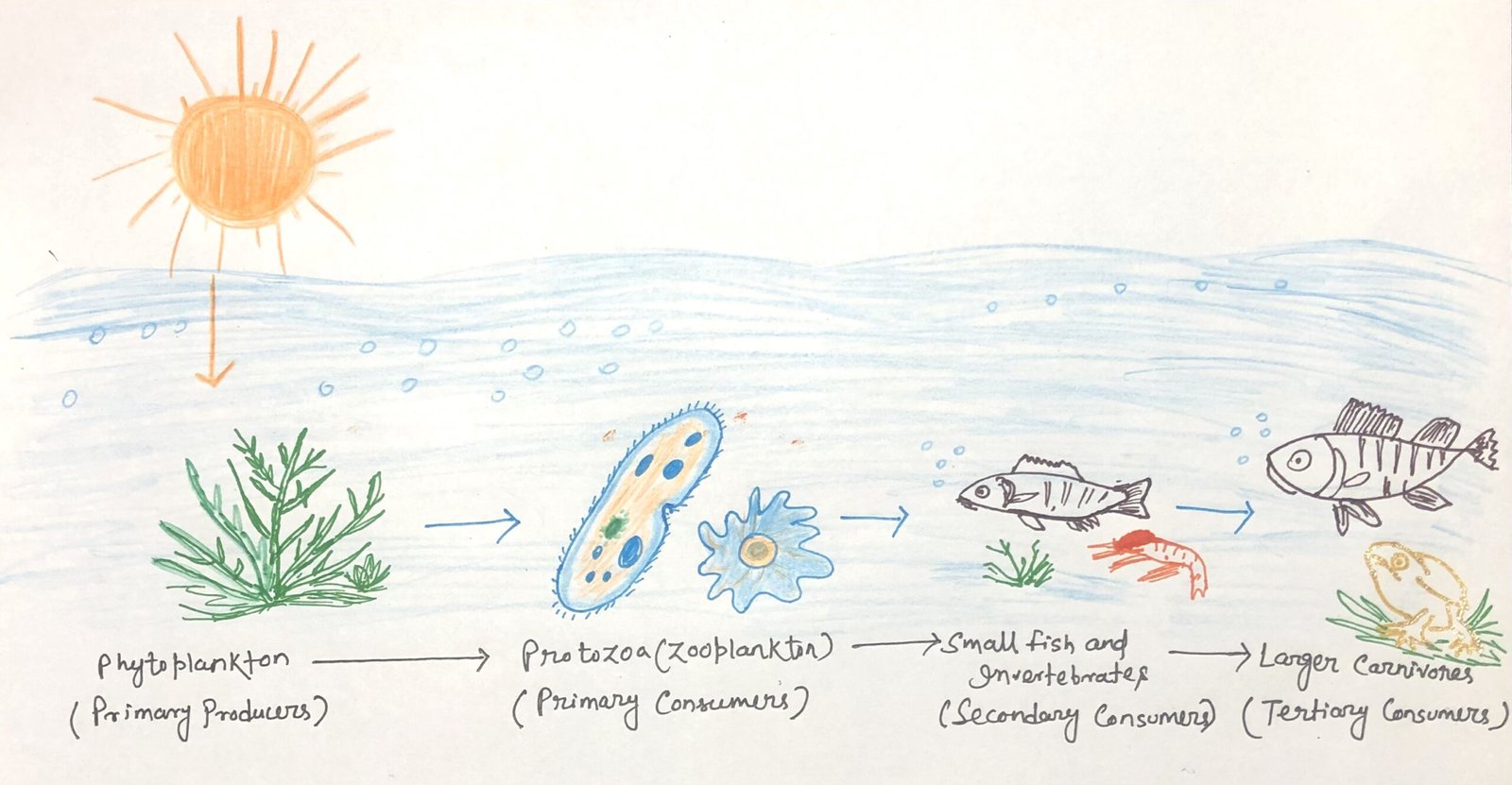
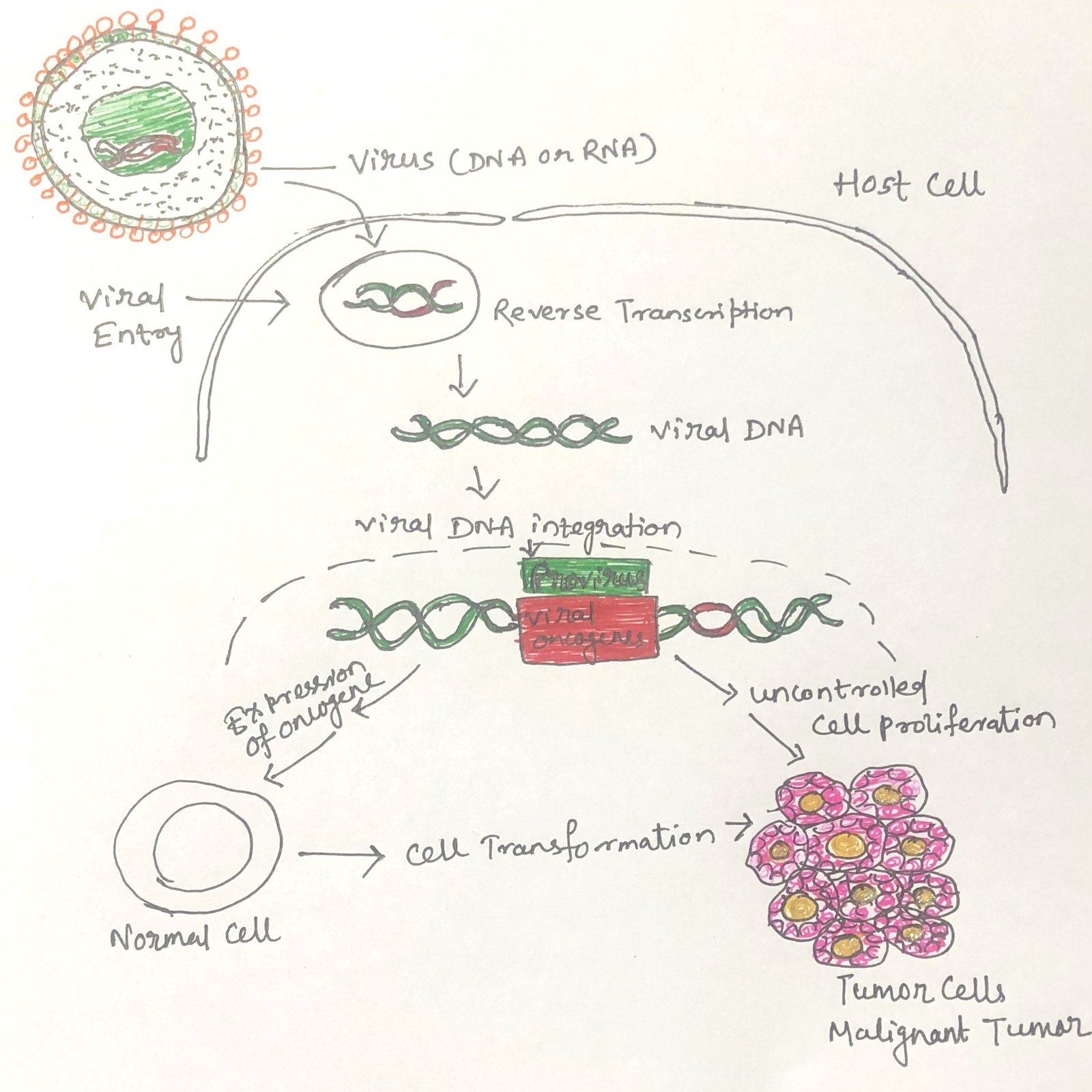
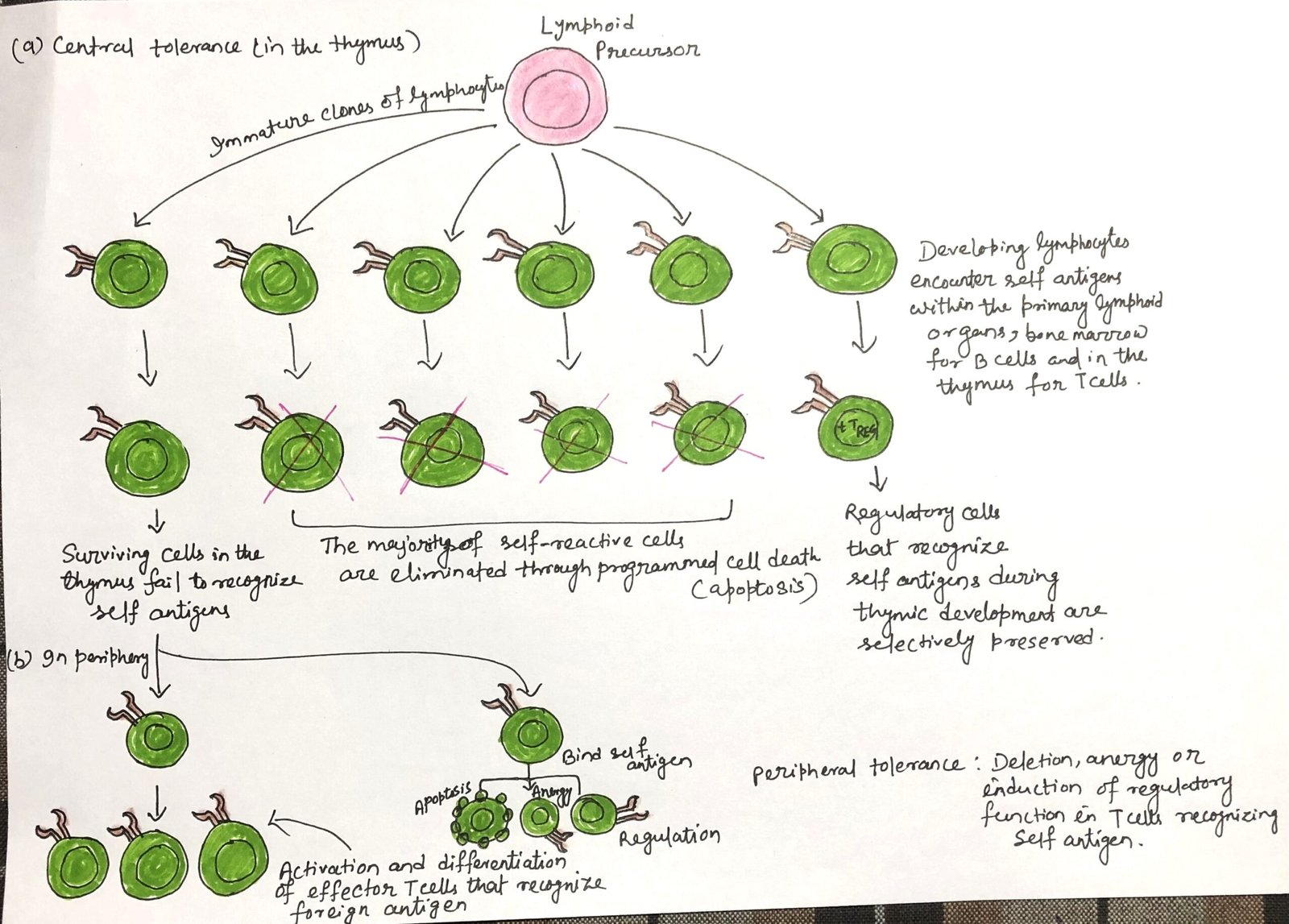
Coliform Bacteria as Indicators of Water Quality
This article provides a brief description of coliform bacteria as indicators of water quality and outlines the standard bacteriological techniques used for their detection and enumeration. Water intended for human consumption must meet strict microbiological standards to ensure safety and prevent disease transmission. Coliform bacteria serve as important indicator organisms for evaluating fecal contamination in … Read more >>