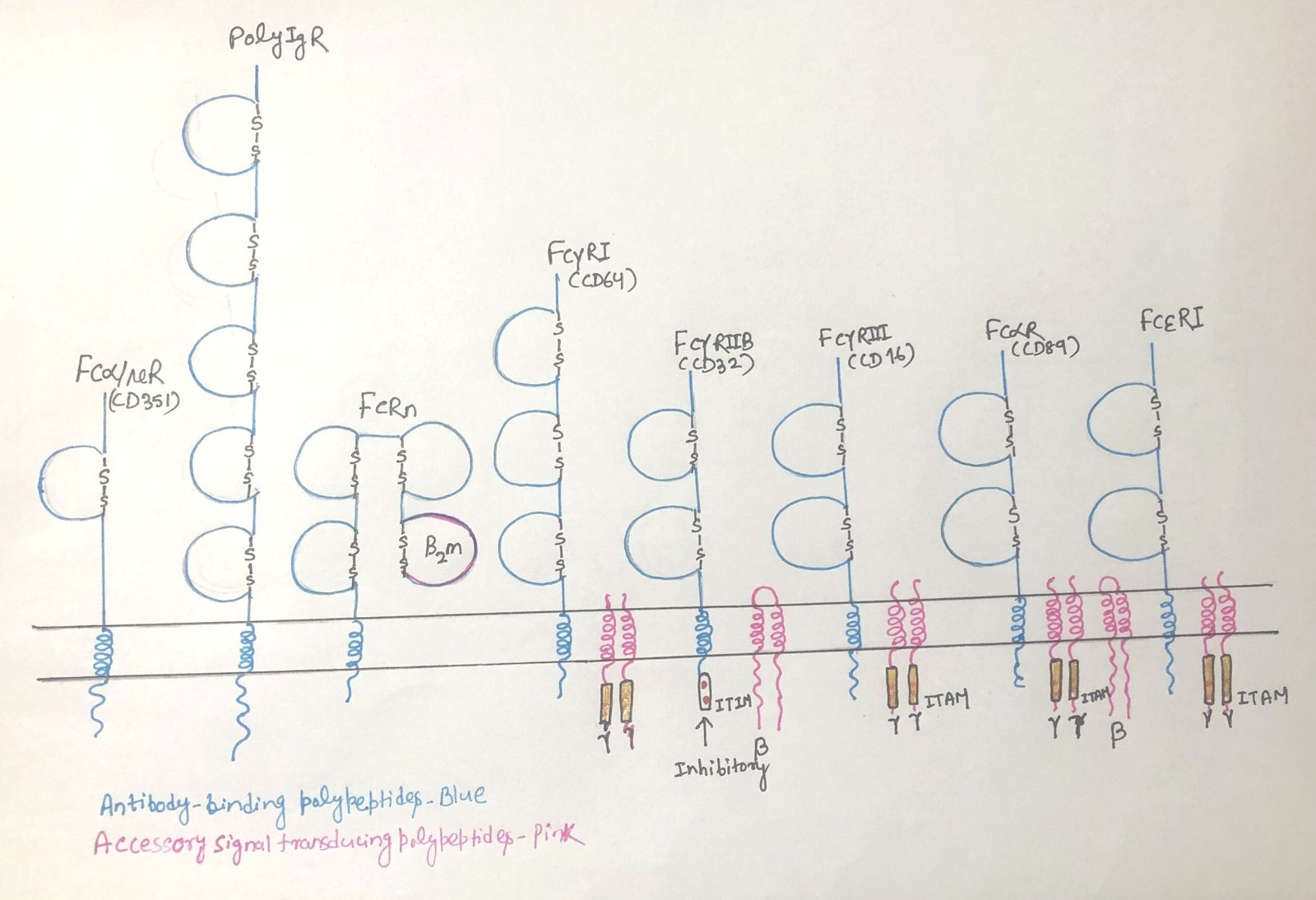
Role of Fc Receptors in Antibody Effector Functions
In this article, I briefly describe the role of Fc receptors in antibody effector functions. Fc receptors (FcRs) are specialized cell-surface receptors that bind to the Fc region of antibodies and link humoral immunity with cellular immune responses. By interacting with different antibody classes, FcRs regulate key immune functions, such as phagocytosis, cytotoxicity, inflammation, and … Read more >>