Protective Role of HDL in Cholesterol Transport
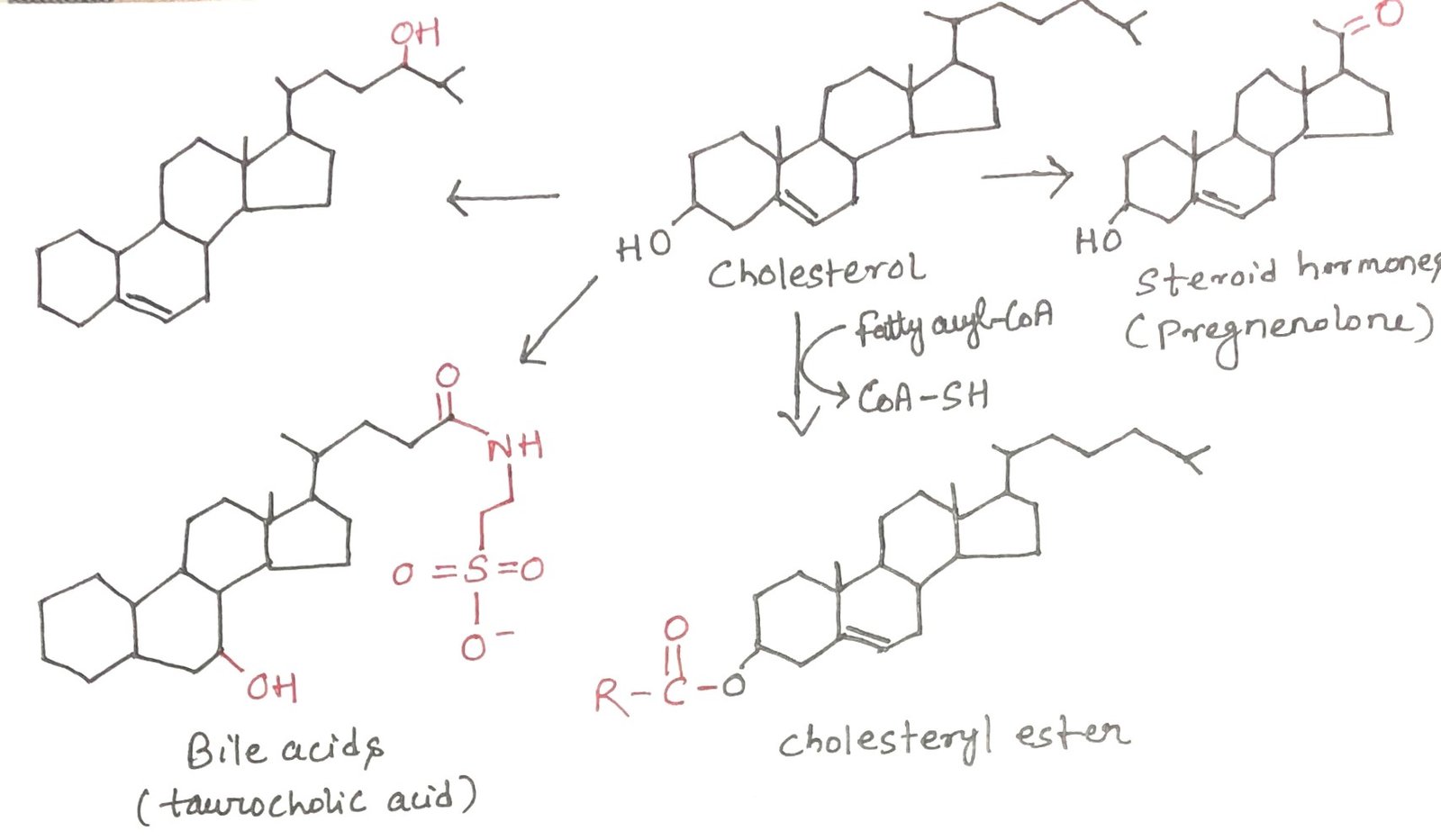
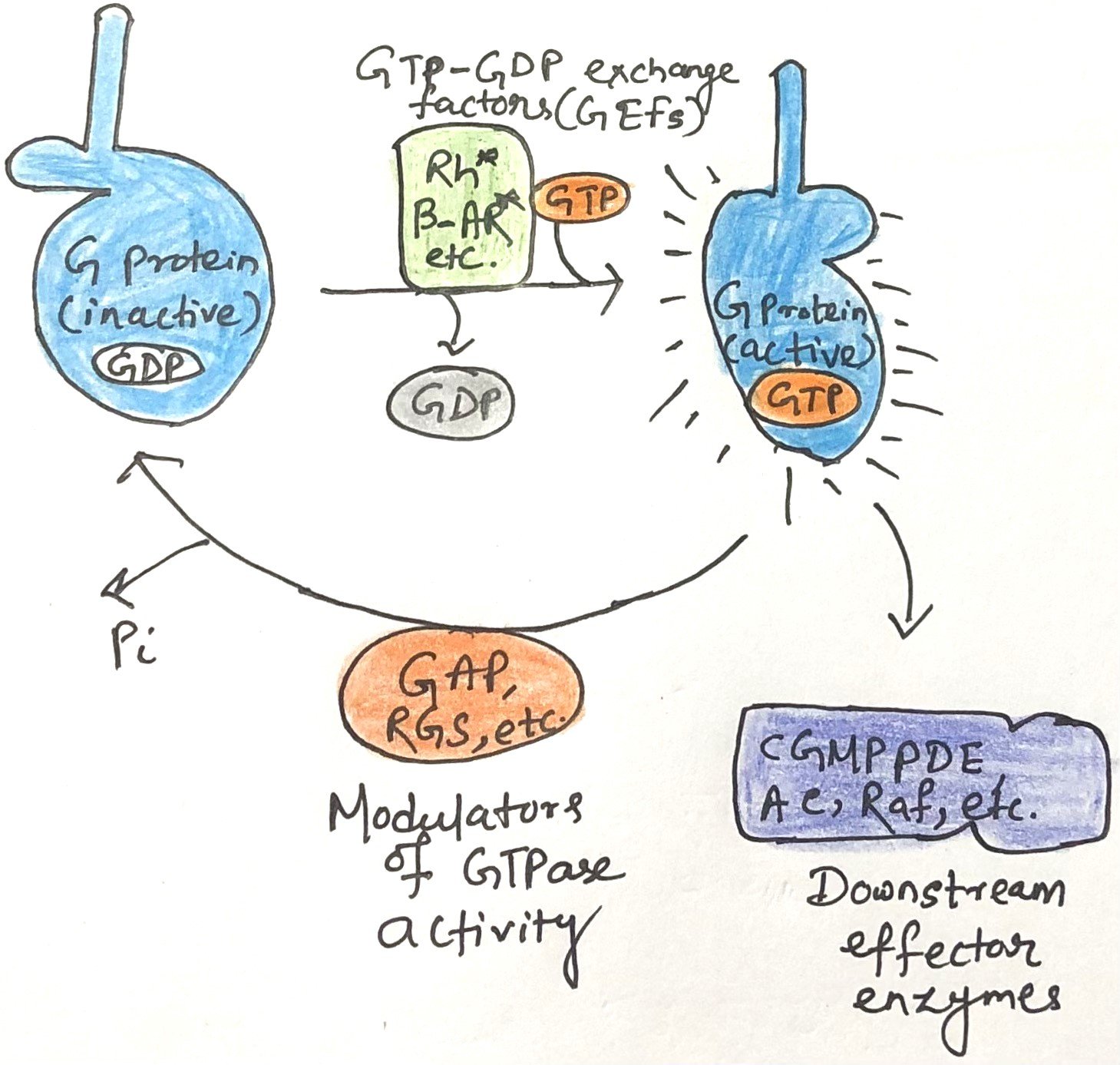
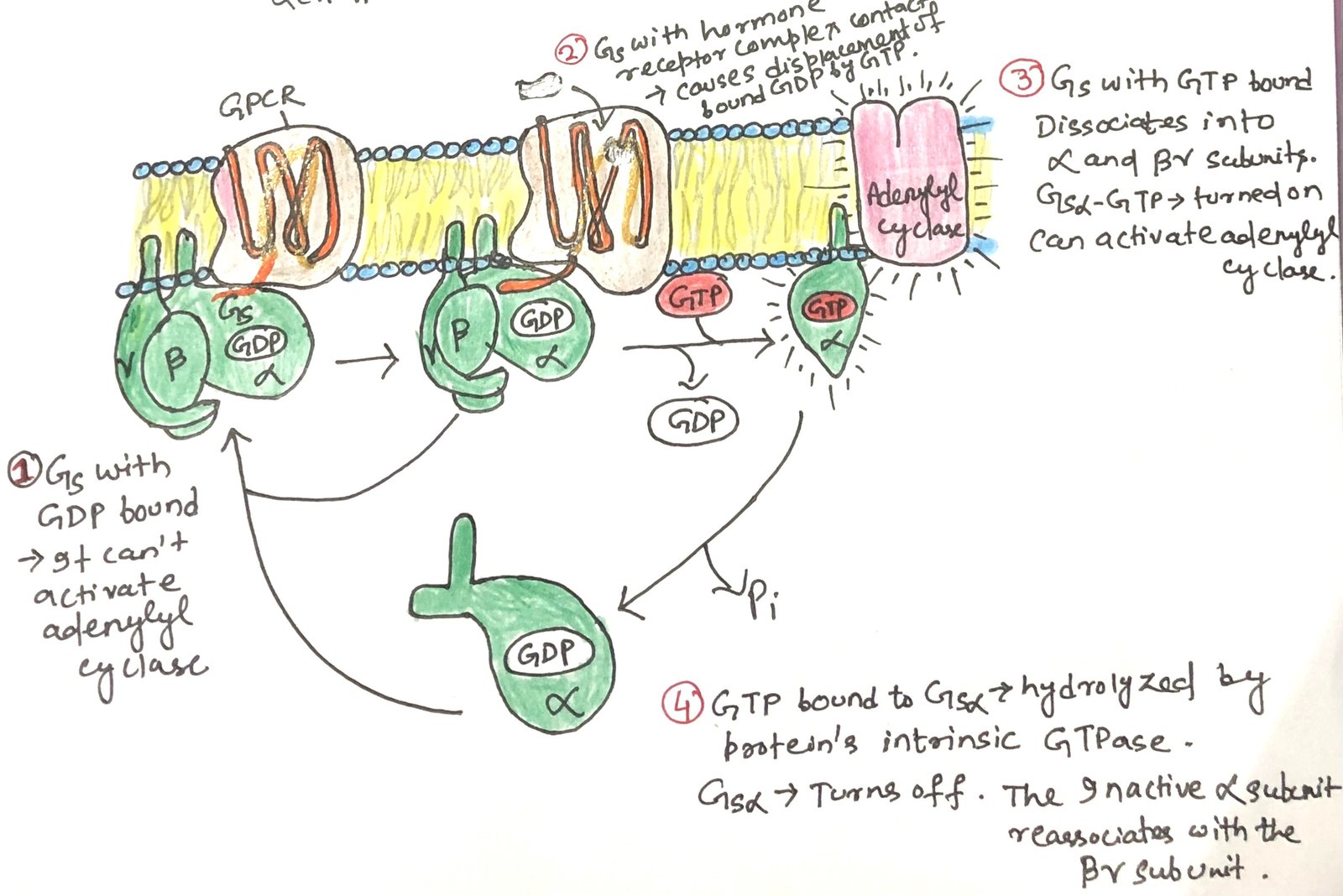
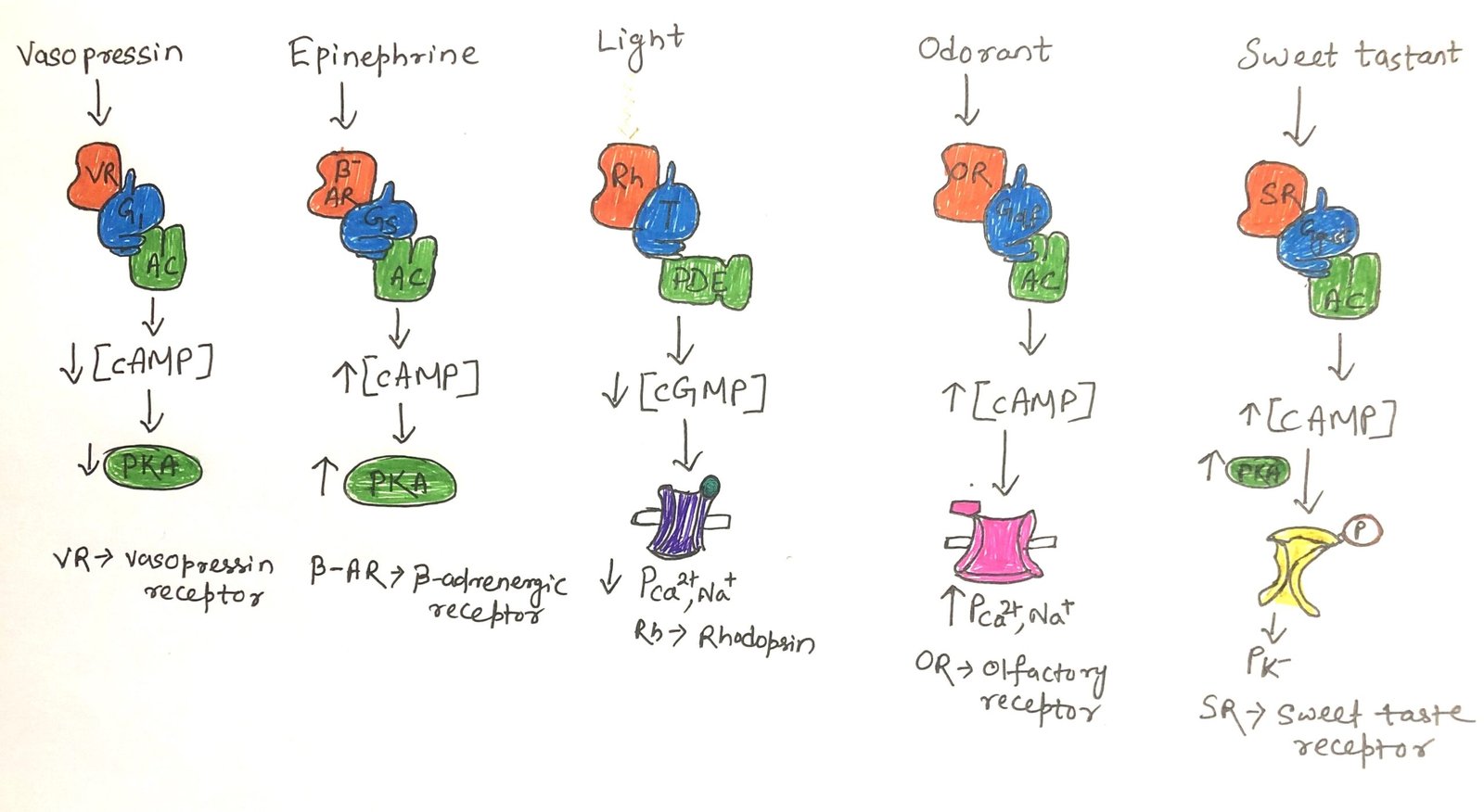
In this article, I provide a brief description of high-density lipoproteins and reverse cholesterol transport. Cholesterol is an essential lipid required for maintaining membrane integrity, synthesizing hormones, and forming bile acids, but its excess is detrimental. Maintaining cholesterol balance depends on coordinated synthesis, transport by lipoproteins, and elimination. This article examines cholesterol transport pathways, the … Read more >>